An organization would like to store customer data on a separate part of the network that is not accessible to users on the main corporate network. Which of the following should the administrator use to accomplish this goal?
A. Segmentation
B. Isolation
C. Patching
D. Encryption
Explanation: Segmentation is a network design technique that divides the network into smaller and isolated segments based on logical or physical boundaries. Segmentation can help improve network security by limiting the scope of an attack, reducing the attack surface, and enforcing access control policies. Segmentation can also enhance network performance, scalability, and manageability. To accomplish the goal of storing customer data on a separate part of the network, the administrator can use segmentation technologies such as subnetting, VLANs, firewalls, routers, or switches. References: CompTIA Security+ Study Guide: Exam SY0-701, 9th Edition, page 308-309 1
An organization is leveraging a VPN between its headquarters and a branch location. Which of the following is the VPN protecting?
A. Data in use
B. Data in transit
C. Geographic restrictions
D. Data sovereignty
Explanation: Data in transit is data that is moving from one location to another, such as over a network or through the air. Data in transit is vulnerable to interception, modification, or theft by malicious actors. A VPN (virtual private network) is a technology that protects data in transit by creating a secure tunnel between two endpoints and encrypting the data that passes through it2. References: CompTIA Security+ Study Guide: Exam SY0-701, 9th Edition, Chapter 4, page 145.
A company has begun labeling all laptops with asset inventory stickers and associating them with employee IDs. Which of the following security benefits do these actions provide? (Choose two.)
A. If a security incident occurs on the device, the correct employee can be notified.
B. The security team will be able to send user awareness training to the appropriate device.
C. Users can be mapped to their devices when configuring software MFA tokens.
D. User-based firewall policies can be correctly targeted to the appropriate laptops.
E. When conducting penetration testing, the security team will be able to target the desired laptops.
F. Company data can be accounted for when the employee leaves the organization.
Explanation: Labeling all laptops with asset inventory stickers and associating them with employee IDs can provide several security benefits for a company. Two of these benefits are:
A. If a security incident occurs on the device, the correct employee can be notified.
An asset inventory sticker is a label that contains a unique identifier for a laptop, such as a serial number, a barcode, or a QR code. By associating this identifier with an employee ID, the security team can easily track and locate the owner of the laptop in case of a security incident, such as a malware infection, a data breach, or a theft. This way, the security team can notify the correct employee about the incident, and provide them with the necessary instructions or actions to take, such as changing passwords, scanning for viruses, or reporting the loss. This can help to contain the incident, minimize the damage, and prevent further escalation.
F. Company data can be accounted for when the employee leaves the organization. When an employee leaves the organization, the company needs to ensure that all the company data and assets are returned or deleted from the employee’s laptop. By labeling the laptop with an asset inventory sticker and associating it with an employee ID, the company can easily identify and verify the laptop that belongs to the departing employee, and perform the appropriate data backup, wipe, or transfer procedures. This can help to protect the company data from unauthorized access, disclosure, or misuse by the former employee or any other party.
The other options are not correct because they are not related to the security benefits of labeling laptops with asset inventory stickers and associating them with employee IDs. B. The security team will be able to send user awareness training to the appropriate device.
User awareness training is a type of security education that aims to improve the knowledge
and behavior of users regarding security threats and best practices. The security team can send user awareness training to the appropriate device by using the email address, username, or IP address of the device, not the asset inventory sticker or the employee ID.
C. Users can be mapped to their devices when configuring software MFA tokens. Software MFA tokens are a type of multi-factor authentication that uses a software application to generate a one-time password or a push notification for verifying the identity of a user. Users can be mapped to their devices when configuring software MFA tokens by using the device ID, phone number, or email address of the device, not the asset inventory sticker or the employee ID. D. User-based firewall policies can be correctly targeted to the appropriate laptops. User-based firewall policies are a type of firewall rules that apply to specific users or groups of users, regardless of the device or location they use to access the network. User-based firewall policies can be correctly targeted to the appropriate laptops by using the username, domain, or certificate of the user, not the asset inventory sticker or the employee ID. E. When conducting penetration testing, the security team will be able to target the desired laptops. Penetration testing is a type of security assessment that simulates a real-world attack on a network or system to identify and exploit vulnerabilities. When conducting penetration testing, the security team will be able to target the desired laptops by using the IP address, hostname, or MAC address of the laptop, not the asset inventory sticker or the employee ID.
References = CompTIA Security+ Study Guide (SY0-701), Chapter 1: General Security Concepts, page 17. Professor Messer’s CompTIA SY0-701 Security+ Training Course, Section 1.4: Asset Management, video: Asset Inventory (6:12).
A security engineer is working to address the growing risks that shadow IT services are introducing to the organization. The organization has taken a cloud-first approach end does not have an on-premises IT infrastructure. Which of the following would best secure the organization?
A. Upgrading to a next-generation firewall
B. Deploying an appropriate in-line CASB solution
C. Conducting user training on software policies
D. Configuring double key encryption in SaaS platforms
Explanation: A Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) solution is the most suitable option for securing an organization that has adopted a cloud-first strategy and does not have an on-premises IT infrastructure. CASBs provide visibility and control over shadow IT services, enforce security policies, and protect data across cloud services.
References = CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 study materials, particularly in the domain of cloud security and managing risks associated with shadow IT.
An administrator at a small business notices an increase in support calls from employees who receive a blocked page message after trying to navigate to a spoofed website. Which of the following should the administrator do?
A. Deploy multifactor authentication.
B. Decrease the level of the web filter settings
C. Implement security awareness training.
D. Update the acceptable use policy
Explanation: In this scenario, employees are attempting to navigate to spoofed websites, which is being blocked by the web filter. To address this issue, the administrator should implement security awareness training. Training helps employees recognize phishing and other social engineering attacks, reducing the likelihood that they will attempt to access malicious websites in the future.
Deploying multifactor authentication (MFA) would strengthen authentication but does not directly address user behavior related to phishing websites. Decreasing the level of the web filter would expose the organization to more threats.
Updating the acceptable use policy may clarify guidelines but is not as effective as hands-on training for improving user behavior.
Select the appropriate attack and remediation from each drop-down list to label the corresponding attack with its remediation.
INSTRUCTIONS
Not all attacks and remediation actions will be used.
If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All button.
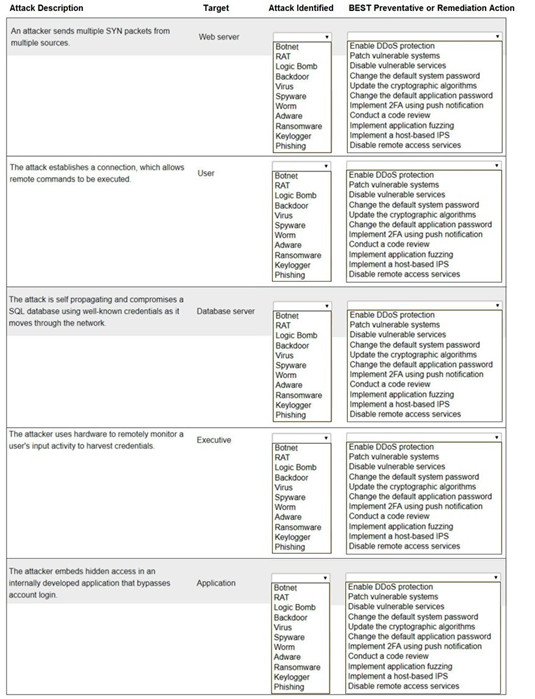
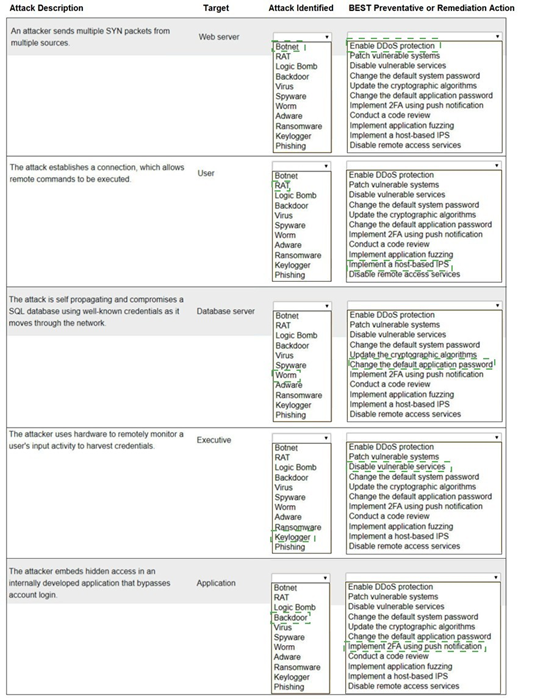
Explanation:
Web serverBotnet Enable DDoS protectionUser RAT Implement a host-based IPS Database server Worm Change the default application passwordExecutive KeyloggerDisable vulnerable servicesApplication Backdoor Implement 2FA using push notification
A software developer would like to ensure. The source code cannot be reverse engineered or debugged. Which of the following should the developer consider?
A. Version control
B. Obfuscation toolkit
C. Code reuse
D. Continuous integration
E. Stored procedures
Explanation: An obfuscation toolkit is used by developers to make source code difficult to understand and reverse engineer. This technique involves altering the code's structure and naming conventions without changing its functionality, making it much harder for attackers to decipher the code or use debugging tools to analyze it. Obfuscation is an important practice in protecting proprietary software and intellectual property from reverse engineering.
References = CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 Course Content: Domain 03 Security Architecture. CompTIA Security+ SY0-601 Study Guide: Chapter on Secure Coding Practices.
Which of the following should a security administrator adhere to when setting up a new set of firewall rules?
A. Disaster recovery plan
B. Incident response procedure
C. Business continuity plan
D. Change management procedure
Explanation: A change management procedure is a set of steps and guidelines that a security administrator should adhere to when setting up a new set of firewall rules. A firewall is a device or software that can filter, block, or allow network traffic based on predefined rules or policies. A firewall rule is a statement that defines the criteria and action for a firewall to apply to a packet or a connection. For example, a firewall rule can allow or deny traffic based on the source and destination IP addresses, ports, protocols, or applications. Setting up a new set of firewall rules is a type of change that can affect the security, performance, and functionality of the network. Therefore, a change management procedure is necessary to ensure that the change is planned, tested, approved, implemented, documented, and reviewed in a controlled and consistent manner. A change management procedure typically includes the following elements:
A change request that describes the purpose, scope, impact, and benefits of the change, as well as the roles and responsibilities of the change owner, implementer, and approver.
A change assessment that evaluates the feasibility, risks, costs, and dependencies of the change, as well as the alternatives and contingency plans.
A change approval that authorizes the change to proceed to the implementation stage, based on the criteria and thresholds defined by the change policy.
A change implementation that executes the change according to the plan and schedule, and verifies the results and outcomes of the change.
A change documentation that records the details and status of the change, as well as the lessons learned and best practices.
A change review that monitors and measures the performance and effectiveness of the change, and identifies any issues or gaps that need to be addressed or improved.
A change management procedure is important for a security administrator to adhere to when setting up a new set of firewall rules, as it can help to achieve the following objectives:
Enhance the security posture and compliance of the network by ensuring that the firewall rules are aligned with the security policies and standards, and that they do not introduce any vulnerabilities or conflicts.
Minimize the disruption and downtime of the network by ensuring that the firewall rules are tested and validated before deployment, and that they do not affect the availability or functionality of the network services or applications.
Improve the efficiency and quality of the network by ensuring that the firewall rules are optimized and updated according to the changing needs and demands of the network users and stakeholders, and that they do not cause any performance or compatibility issues.
Increase the accountability and transparency of the network by ensuring that the firewall rules are documented and reviewed regularly, and that they are traceable and auditable by the relevant authorities and parties.
The other options are not correct because they are not related to the process of setting up a new set of firewall rules. A disaster recovery plan is a set of policies and procedures that aim to restore the normal operations of an organization in the event of a system failure, natural disaster, or other emergency. An incident response procedure is a set of steps and guidelines that aim to contain, analyze, eradicate, and recover from a security incident, such as a cyberattack, data breach, or malware infection. A business continuity plan is a set of strategies and actions that aim to maintain the essential functions and operations of an organization during and after a disruptive event, such as a pandemic, power outage, or civil unrest.
References = CompTIA Security+ Study Guide (SY0-701), Chapter 7: Resilience and Recovery, page 325. Professor Messer’s CompTIA SY0-701 Security+ Training Course, Section 1.3: Security Operations, video: Change Management (5:45).
Which of the following provides the details about the terms of a test with a third-party penetration tester?
A. Rules of engagement
B. Supply chain analysis
C. Right to audit clause
D. Due diligence
Explanation: Rules of engagement are the detailed guidelines and constraints regarding the execution of information security testing, such as penetration testing. They define the scope, objectives, methods, and boundaries of the test, as well as the roles and responsibilities of the testers and the clients. Rules of engagement help to ensure that the test is conducted in a legal, ethical, and professional manner, and that the results are accurate and reliable. Rules of engagement typically include the following elements:
The type and scope of the test, such as black box, white box, or gray box, and the target systems, networks, applications, or data.
The client contact details and the communication channels for reporting issues, incidents, or emergencies during the test.
The testing team credentials and the authorized tools and techniques that they can use.
The sensitive data handling and encryption requirements, such as how to store, transmit, or dispose of any data obtained during the test.
The status meeting and report schedules, formats, and recipients, as well as the confidentiality and non-disclosure agreements for the test results.
The timeline and duration of the test, and the hours of operation and testing windows.
The professional and ethical behavior expectations for the testers, such as avoiding unnecessary damage, disruption, or disclosure of information.
Supply chain analysis, right to audit clause, and due diligence are not related to the terms of a test with a third-party penetration tester. Supply chain analysis is the process of evaluating the security and risk posture of the suppliers and partners in a business network. Right to audit clause is a provision in a contract that gives one party the right to audit another party to verify their compliance with the contract terms and conditions. Due diligence is the process of identifying and addressing the cyber risks that a potential vendor or partner brings to an organization.
A company is developing a business continuity strategy and needs to determine how many staff members would be required to sustain the business in the case of a disruption. Which of the following best describes this step?
A. Capacity planning
B. Redundancy
C. Geographic dispersion
D. Tablet exercise
Explanation: Capacity planning is the process of determining the resources needed to meet the current and future demands of an organization. Capacity planning can help a company develop a business continuity strategy by estimating how many staff members would be required to sustain the business in the case of a disruption, such as a natural disaster, a cyberattack, or a pandemic. Capacity planning can also help a company optimize the use of its resources, reduce costs, and improve performance.
References = CompTIA Security+ Study Guide with over 500 Practice Test Questions: Exam SY0-701, 9th Edition, Chapter 4, page 184. CompTIA Security+ (SY0- 701) Certification Exam Objectives, Domain 4.1, page 14. Business Continuity – SY0-601 CompTIA Security+ : 4.1
| Page 3 out of 39 Pages |
| Previous |