Which two key exchange algorithms consume the most resources when decrypting SSL traffic? (Choose two.)
A. ECDSA
B. ECDHE
C. RSA
D. DHE
Explanation:
The two key exchange algorithms that consume the most resources when decrypting SSL
traffic are ECDHE and DHE. These are both Diffie-Hellman based algorithms that enable
perfect forward secrecy (PFS), which means that they generate a new and unique session
key for each SSL/TLS session, and do not reuse any previous keys. This enhances the
security of the encrypted communication, but also increases the computational cost and
complexity of the key exchange process. ECDHE stands for Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman
Ephemeral, which uses elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) to generate the session key. DHE
stands for Diffie-Hellman Ephemeral, which uses modular arithmetic to generate the
session key. Both ECDHE and DHE require more CPU and memory resources than RSA,
which is a non-PFS algorithm that uses public and private keys to encrypt and decrypt the
session key.
References:
Key Exchange Algorithms, Best Practices for Enabling SSL
Decryption, PCNSE Study Guide (page 60)
An auditor is evaluating the configuration of Panorama and notices a discrepancy between the Panorama template and the local firewall configuration. When overriding the firewall configuration pushed from Panorama, what should you consider?
A. The firewall template will show that it is out of sync within Panorama.
B. The modification will not be visible in Panorama.
C. Only Panorama can revert the override.
D. Panorama will update the template with the overridden value.
Explanation:
When managing firewalls with Panorama, configurations can be pushed from
Panorama templates to managed firewalls. However, there are scenarios where specific
settings need to be overridden on the local firewall level due to unique requirements or
exceptions.
B. The modification will not be visible in Panorama:
When an override is made directly on the firewall, this change is not automatically
reflected back in Panorama's templates or device groups. The local configuration
on the firewall will take precedence over the Panorama pushed configuration for
the overridden settings, but these local changes will not be visible in the Panorama
interface. This means that while Panorama maintains central control and visibility
over the bulk of the configuration, it does not have visibility into local overrides
made directly on the firewalls.
This distinction is crucial for auditors and administrators to understand, as it impacts how
configurations are managed and synchronized between Panorama and the individual
firewalls. Local overrides provide flexibility but require careful management to ensure
consistency and compliance with security policies.
Which two policy components are required to block traffic in real time using a dynamic user group (DUG)? (Choose two.)
A. A Deny policy for the tagged traffic
B. An Allow policy for the initial traffic
C. A Decryption policy to decrypt the traffic and see the tag
D. A Deny policy with the "tag" App-ID to block the tagged traffic
Explanation: Use the dynamic user group in a policy to regulate traffic for the members of the group. You will need to configure at least two rules: one to allow initial traffic to populate the dynamic user group and one to deny traffic for the activity you want to prevent (in this case, questionable-activity). To tag users, the rule to allow traffic must have a higher rule number in your rule base than the rule that denies traffic.
A remote administrator needs access to the firewall on an untrust interface. Which three options would you configure on an interface Management profile to secure management access? (Choose three)
A. HTTPS
B. SSH
C. Permitted IP Addresses
D. HTTP
E. User-IO
Exhibit.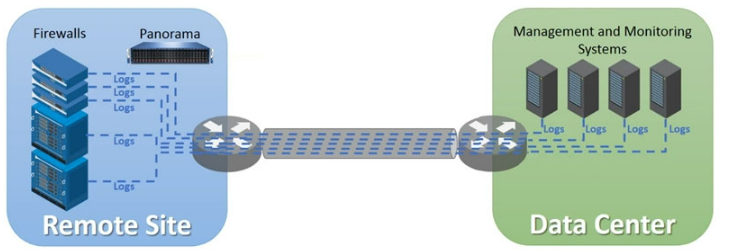
An organization has Palo Alto Networks NGFWs that send logs to remote monitoring and
security management platforms The network team has reported excessive traffic on the
corporate WAN How could the Palo Alto Networks NGFW administrator reduce WAN traffic
while maintaining support for all the existing monitoring/security platforms?
A. Any configuration on an M-500 would address the insufficient bandwidth concerns
B. Forward logs from external sources to Panorama for correlation, and from Panorama send them to the NGFW
C. Configure log compression and optimization features on all remote firewalls
D. Forward logs from firewalls only to Panorama and have Panorama forward logs to other external services
Refer to the exhibit.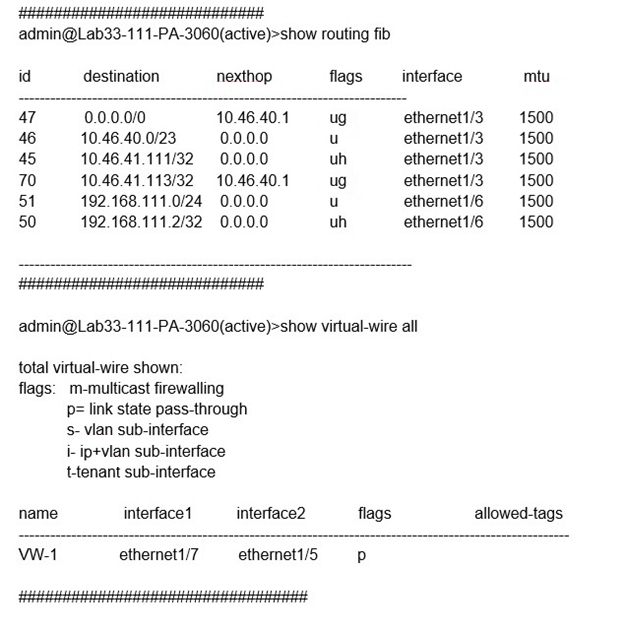
Which will be the egress interface if the traffic's ingress interface is ethernet1/7 sourcing
from 192.168.111.3 and to the destination 10.46.41.113?
A. ethernet1/6
B. ethernet1/3
C. ethernet1/7
D. ethernet1/5
Explanation: In the second image, VW ports mentioned are 1/5 and 1/7. Hence it can not be a part of any other routing. So if any traffic coming as ingress from 1/7, it has to go out via 1/5. The egress interface for the traffic with ingress interface ethernet1/7, source 192.168.111.3, and destination 10.46.41.113 will be ethernet1/5. This is because the traffic will match the virtual wire with interfaces ethernet1/5 and ethernet1/7, which is configured to allow VLAN-tagged traffic with tags 10 and 201. The traffic will also match the security policy rule that allows traffic from zone Trust to zone Untrust, which are assigned to ethernet1/7 and ethernet1/5 respectively2. Therefore, the traffic will be forwarded to the same interface from which it was received, which is ethernet1/53.
A firewall administrator wants to be able at to see all NAT sessions that are going ‘through a firewall with source NAT. Which CLI command can the administrator use?
A. show session all filter nat-rule-source
B. show running nat-rule-ippool rule "rule_name
C. show running nat-policy
D. show session all filter nat source
A superuser is tasked with creating administrator accounts for three contractors. For compliance purposes, all three contractors will be working with different device-groups in their hierarchy to deploy policies and objects. Which type of role-based access is most appropriate for this project?
A. Create a Dynamic Read only superuser
B. Create a Dynamic Admin with the Panorama Administrator role
C. Create a Device Group and Template Admin
D. Create a Custom Panorama Admin
Explanation: Custom Panorama Admin: Custom Panorama Admin roles allow you to customize the elements of Panorama that an administrator can access. You can hide tabs in the web interface, you can set specific items in Panorama to read-only, or you can limit an administrator’s access to Panorama plugins. Custom Panorama Admin roles require planning and configuration, but they provide extensive flexibility because you can control what administrators can access through the web interface or the CLI. Device Group and Template Admin: Device Group and Template Admin roles also require configuration because there are no built-in examples. These Admin Roles allow you to define which Panorama templates or Panorama device groups an administrator can access and configure. You can hide tabs in the web interface or set specific items to read only to control what administrators can configure.
What would allow a network security administrator to authenticate and identify a user with a new BYOD-type device that is not joined to the corporate domain?
A. an Authentication policy with 'unknown' selected in the Source User field
B. an Authentication policy with 'known-user' selected in the Source User field
C. a Security policy with 'known-user' selected in the Source User field
D. a Security policy with 'unknown' selected in the Source User field
Explanation: For a network security administrator to authenticate and identify a user with a
new BYOD-type device that is not joined to the corporate domain, the most effective
method is to use an Authentication policy targeting users not yet identified by the system.
A. an Authentication policy with 'unknown' selected in the Source User field:
An Authentication policy allows the firewall to challenge unidentified users for
credentials. By selecting 'unknown' in the Source User field, the policy targets
users who have not yet been identified by the firewall, which would include users
on new BYOD devices not joined to the domain.
Once the user provides valid credentials, the firewall can authenticate the user and
map their identity to subsequent sessions, enabling the application of user-based
policy rules and monitoring.
This approach ensures that new and unknown devices can be properly authenticated and
identified without compromising security or requiring the device to be part of the corporate
domain.
Which GloDalProtecI gateway setting is required to enable split-tunneting by access route, destination domain and application?
A. Tunnel mode
B. Satellite mode
C. IPSec mode
D. No Direct Access to local networks
| Page 2 out of 30 Pages |
| Previous |