A company wants to move its Mule API implementations into production as quickly as
possible. To protect access to all Mule application data and metadata, the company
requires that all Mule applications be deployed to the company's customer-hosted
infrastructure within the corporate firewall. What combination of runtime plane and control
plane options meets these project lifecycle goals?
A.
Manually provisioned customer-hosted runtime plane and customer-hosted control plane
B.
MuleSoft-hosted runtime plane and customer-hosted control plane
C.
Manually provisioned customer-hosted runtime plane and MuleSoft-hosted control plane
D.
iPaaS provisioned customer-hosted runtime plane and MuleSoft-hosted control plane
What is a best practice when building System APIs?
A.
Document the API using an easily consumable asset like a RAML definition
B.
Model all API resources and methods to closely mimic the operations of the backend system
C.
Build an Enterprise Data Model (Canonical Data Model) for each backend system and apply it to System APIs
D.
Expose to API clients all technical details of the API implementation's interaction wifch
the backend system
An organization uses various cloud-based SaaS systems and multiple on-premises
systems. The on-premises systems are an important part of the organization's application
network and can only be accessed from within the organization's intranet.
What is the best way to configure and use Anypoint Platform to support integrations with
both the cloud-based SaaS systems and on-premises systems?
A) Use CloudHub-deployed Mule runtimes in an Anypoint VPC managed by Anypoint
Platform Private Cloud Edition control plane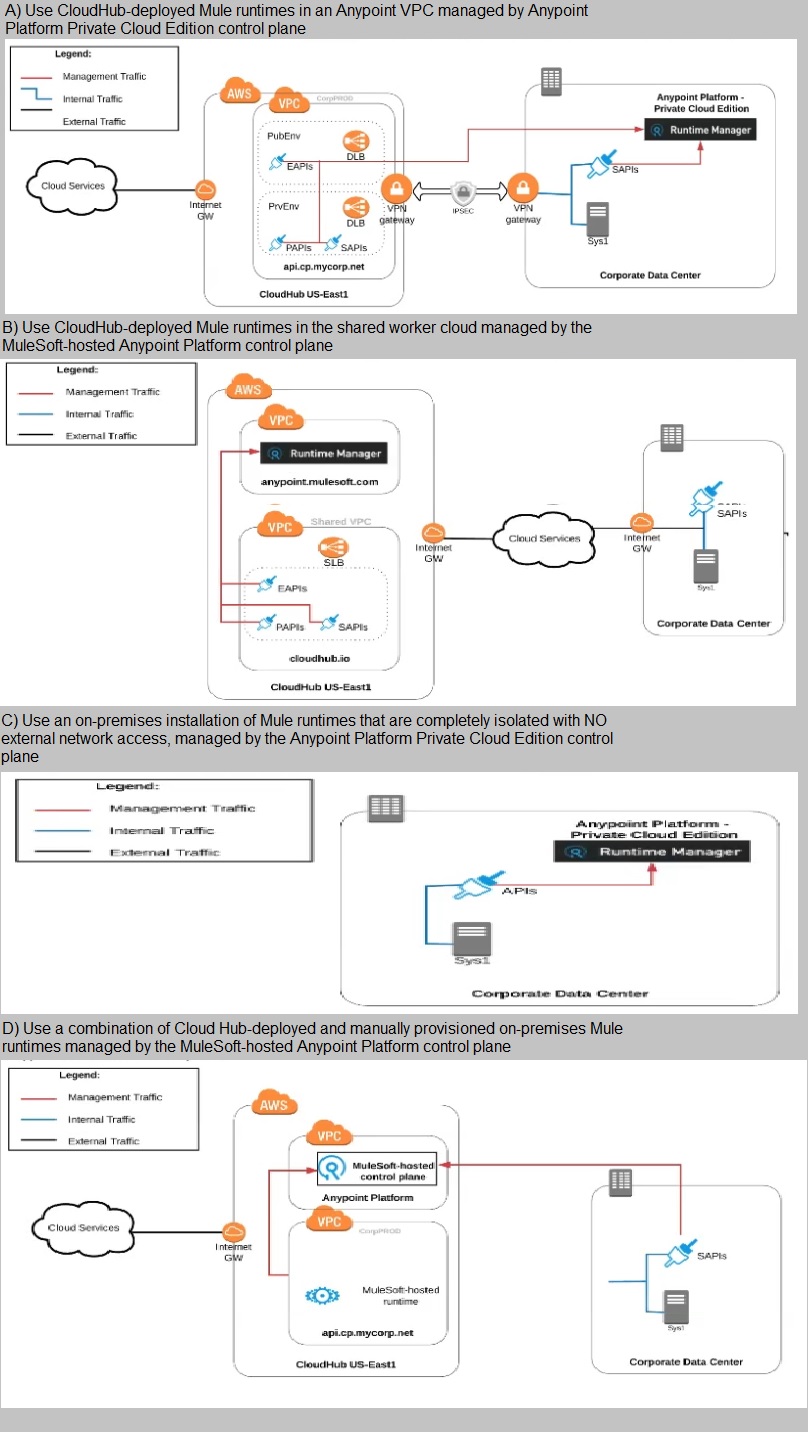
A.
Option A
B.
Option B
C.
Option C
D.
Option D
An organization has implemented a Customer Address API to retrieve customer address
information. This API has been deployed to multiple environments and has been configured
to enforce client IDs everywhere.
A developer is writing a client application to allow a user to update their address. The
developer has found the Customer Address API in Anypoint Exchange and wants to use it
in their client application.
What step of gaining access to the API can be performed automatically by Anypoint
Platform?
A.
Approve the client application request for the chosen SLA tier
B.
Request access to the appropriate API Instances deployed to multiple environments using the client application's credentials
C.
Modify the client application to call the API using the client application's credentials
D.
Create a new application in Anypoint Exchange for requesting access to the API
What is a key requirement when using an external Identity Provider for Client Management in Anypoint Platform?
A.
Single sign-on is required to sign in to Anypoint Platform
B.
The application network must include System APIs that interact with the Identity
Provider
C.
To invoke OAuth 2.0-protected APIs managed by Anypoint Platform, API clients must submit access tokens issued by that same Identity Provider
D.
APIs managed by Anypoint Platform must be protected by SAML 2.0 policies
Which of the following best fits the definition of API-led connectivity?
A.
API-led connectivity is not just an architecture or technology but also a way to organize people and processes for efficient IT delivery in the organization
B.
API-led connectivity is a 3-layered architecture covering Experience, Process and System layers
C.
API-led connectivity is a technology which enabled us to implement Experience, Process and System layer based APIs
An organization wants MuleSoft-hosted runtime plane features (such as HTTP load balancing, zero downtime, and horizontal and vertical scaling) in its Azure environment. What runtime plane minimizes the organization's effort to achieve these features?
A.
Anypoint Runtime Fabric
B.
Anypoint Platform for Pivotal Cloud Foundry
C.
CloudHub
D.
A hybrid combination of customer-hosted and MuleSoft-hosted Mule runtimes
What is a key performance indicator (KPI) that measures the success of a typical C4E that is immediately apparent in responses from the Anypoint Platform APIs?
A.
The number of production outage incidents reported in the last 24 hours
B.
The number of API implementations that have a publicly accessible HTTP endpoint and are being managed by Anypoint Platform
C.
The fraction of API implementations deployed manually relative to those deployed using a CI/CD tool
D.
The number of API specifications in RAML or OAS format published to Anypoint
Exchange
An organization has created an API-led architecture that uses various API layers to integrate mobile clients with a backend system. The backend system consists of a number of specialized components and can be accessed via a REST API. The process and
experience APIs share the same bounded-context model that is different from the backend
data model. What additional canonical models, bounded-context models, or anti-corruption
layers are best added to this architecture to help process data consumed from the backend
system?
A.
Create a bounded-context model for every layer and overlap them when the boundary
contexts overlap, letting API developers know about the differences between upstream and
downstream data models
B.
Create a canonical model that combines the backend and API-led models to simplify
and unify data models, and minimize data transformations.
C.
Create a bounded-context model for the system layer to closely match the backend data
model, and add an anti-corruption layer to let the different bounded contexts cooperate
across the system and process layers
D.
Create an anti-corruption layer for every API to perform transformation for every data
model to match each other, and let data simply travel between APIs to avoid the complexity
and overhead of building canonical models
What is true about automating interactions with Anypoint Platform using tools such as Anypoint Platform REST APIs, Anypoint CU, or the Mule Maven plugin?
A.
Access to Anypoint Platform APIs and Anypoint CU can be controlled separately through the roles and permissions in Anypoint Platform, so that specific users can get access to Anypoint CLI white others get access to the platform APIs
B.
Anypoint Platform APIs can ONLY automate interactions with CloudHub, while the Mule Maven plugin is required for deployment to customer-hosted Mule runtimes
C.
By default, the Anypoint CLI and Mule Maven plugin are NOT included in the Mule runtime, so are NOT available to be used by deployed Mule applications
D.
API policies can be applied to the Anypoint Platform APIs so that ONLY certain LOBs have access to specific functions
| Page 1 out of 10 Pages |