Refer to the exhibit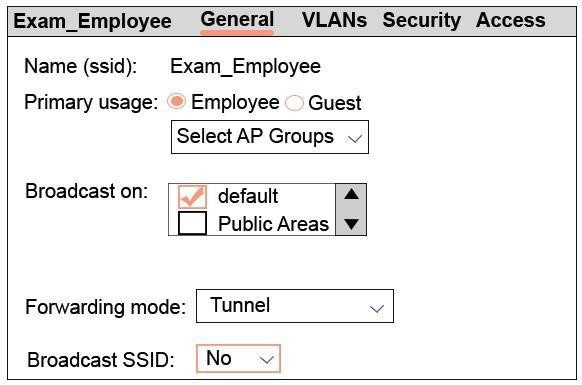
What describes the behavior for this WLAN?
A.
APs in the default group broadcast the SSID. Clients can connect to the WLAN on APs
in the default group only.
B.
No APs broadcast the SSID. Clients cannot connect to the WLAN until administrators
activate it.
C.
No APs broadcast the SSID. Clients can connect to the WLAN on APs in the
default group only.
D.
APs in the default group broadcast the SSID. Clients can connect to the WLAN on APs
in any group.
No APs broadcast the SSID. Clients can connect to the WLAN on APs in the
default group only.
What is a valid way to deploy an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)?
A.
as a subscription-based service through the Aruba cloud
B.
as a role on a Mobility Controller 7030 that is deployed as a standalone controller
C.
as a virtual appliance on a server that meets the recommended hardware requirements
D.
as a role on a Mobility Controller 7240 that is deployed as a master controller
as a virtual appliance on a server that meets the recommended hardware requirements
What is one difference between captive portal authentication and 802.1X authentication?
A.
802.1X authentication always authenticates the wireless client, while captive portal
authentication always authenticates the wireless user.
B.
802.1X authentication occurs at Layer 2, while captive portal authentication occurs at
Layer 3.
C.
802.1X authentication must use an LDAP server, while captive portal authentication can
use a RADIUS server or an LDAP server.
D.
802.1X authentication is typically implemented without encryption, while captive
authentication is often combined with WPA or WPA2.
802.1X authentication occurs at Layer 2, while captive portal authentication occurs at
Layer 3.
A network administrator needs to configure firewall rules for three roles:
✑Finance
✑Sales
✑Employee
Several rules apply to both the Employee and Sales roles, but not to the Finance
role. What is the simplest way to configure these rules?
A.
Define the Employee and Sales roles as internal roles, and then configure the rules as global rules for internal users.
B.
Apply these rules as a subnet-based policy, and then ensure that only Employee and Sales users are assigned IP addresses in that subnet.
C.
Select either the Employee or Sales role, and then configure these rules within the global policy.
D.
Create a policy with these rules, and then apply that policy to the Employee and Sales roles.
Create a policy with these rules, and then apply that policy to the Employee and Sales roles.
Refer to the exhibit.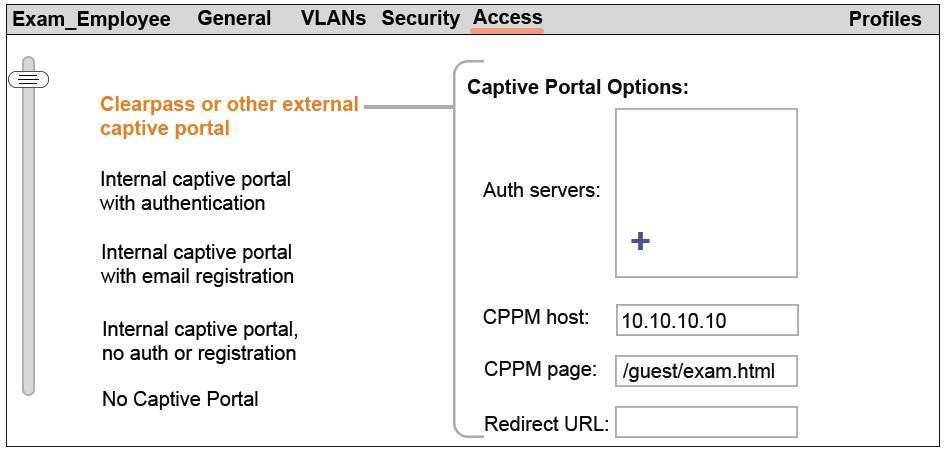
A network administrator creates a guest WLAN on an Aruba Mobility Master (MM). The
exhibit shows some of the settings for the WLAN.
How should the network administrator handle the Auth server settings?
A.
Add an authentication server with the LDAP type and the IP address of the company AD server.
B.
Add an authentication server with the LDAP type and IP address 10.10.10.10.
C.
Add an authentication server with the RADIUS type and IP address 10.10.10.10.
D.
Add an authentication server with the RADIUS type and the IP address of the company AD server.
Add an authentication server with the RADIUS type and IP address 10.10.10.10.
Refer to the exhibit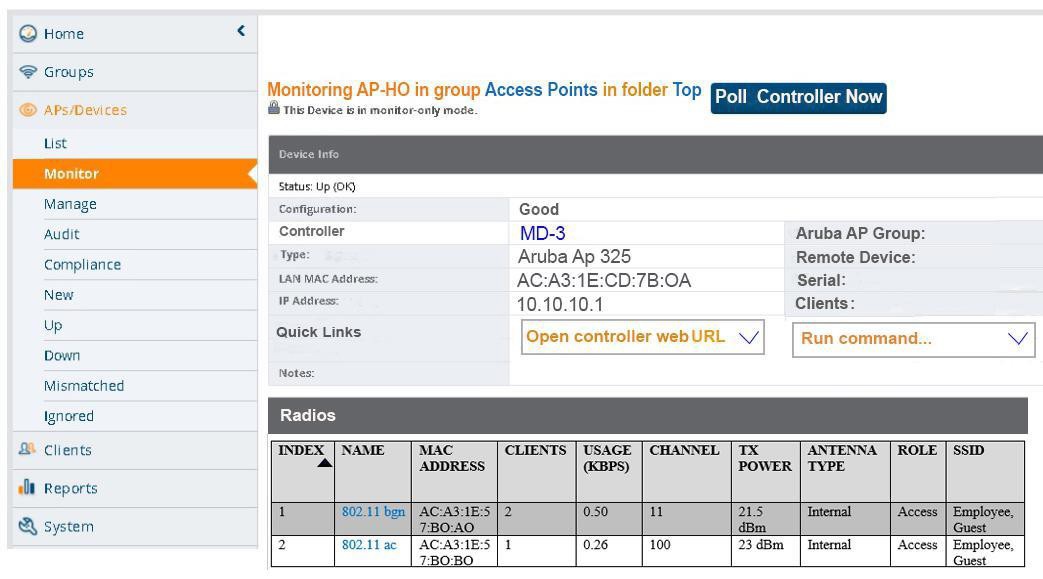
A network administrator needs to use Aruba AirWave to view statistics for an AP’s
802.11ac radio. How can the administrator update the information on-demand rather than
wait the typical interval?
A.
Click Poll Controller Now
B.
Click the 802.11ac link
C.
Log out of the interface and log back in
D.
Refresh the browser
Click Poll Controller Now
A customer has a large campus that requires 400 Aruba 335 APs to support a total of
20,000 wireless users and 12Gbps of traffic. Although the customer wants two controllers
for redundancy, each controller must be able to support all of the APs and users on its own.
Which Aruba Mobility Controller models meet the customer requirements and DO
NOT unnecessarily exceed them?
A.
Aruba 7024 controllers
B.
Aruba 7210 controllers
C.
Aruba 7240 controllers
D.
Aruba 7030 controllers
Aruba 7210 controllers
A company currently uses Instant APs (IAPs), all managed by a virtual controller. The
company expects to double in size without the next 18 months. The network manager
wants to purchase additional APs to service the increased traffic load. The network
manager also wants to deploy a Mobility Controller (MC) to manage all APs.
How should the network administrator adapt the current IAPs to a controlled architecture?
A.
Manage both the MCs and IAP clusters with Aruba Central.
B.
Configure the IAPs to establish CPSec tunnels to the new MCs.
C.
Manage both the MCs and IAP clusters with a Mobility Master (MM).
D.
Convert the IAPs to Campus APs controlled by the new MCs.
Convert the IAPs to Campus APs controlled by the new MCs.
A company plans to deploy a Mobility Master (MM). The MM will manage 50 Mobility
Controller (MC) appliances that will control a total of 700 APs, and 10 Virtual
Mobility Controllers (VMCs) that will control a total of 200 APs.
How many MM licenses does the company require?
A.
60
B.
210
C.
900
D.
960
960
Explanation:
Starting with ArubaOS 8.0.1, the MM license is required to terminate devices (controllers or
APs) on Mobility Master. If the Mobility Master does not have sufficient MM licenses and an
AP fails to obtain a license, that AP can get an IP address and connect to its controller, but
will not broadcast an SSID.
When an Aruba solution uses AirMatch, which device generates the channel and
power plan for an AP?
A.
the AirWave Management Platform
B.
the Mobility Master (MM)
C.
the Mobility Controller (MC) for the AP
D.
the AP itself
the Mobility Master (MM)
| Page 4 out of 13 Pages |
| Previous |