Although the packet listed below contained malware, it freely passed through a layer 3 switch. Why didn’t the switch detect the malware in this packet?

A.
The packet was part of a fragmentation attack
B.
The data portion of the packet was encrypted
C.
The entire packet was corrupted by the malware
D.
It didn’t look deeply enough into the packet
It didn’t look deeply enough into the packet
Routers, layer 3 switches, some firewalls, and other gateways are packet filtering devices that use access control lists (ACLs) and perform packet inspection. This type of device uses a small subset of the packet to make filtering decisions, such as source and destination IP address and protocol. These devices will then allow or deny protocols based on their associated ports. This type of packet inspection and access control is still highly susceptible to malicious attacks, because payloads and other areas of the packet are not being inspected. For example, application level attacks that are tunneled over open ports such as HTTP (port 80) and HTTPS (port 443).
An outside vulnerability assessment reveals that users have been routinely accessing Gmail from work for over a year, a clear violation of this organization’s security policy. The users report “it just started working one day”. Later, a network administrator admits he meant to unblock Gmail for just his own IP address, but he made a mistake in the firewall rule. Which security control failed?
A.
Access control
B.
Authentication
C.
Auditing
D.
Rights management
Auditing
Audits are used to identify irregular activity in logged (after-the-fact) records. If this activity went unnoticed or uncorrected for over a year, the internal audits failed because they were either incomplete or inaccurate. Authentication, access control and managing user rights would not apply as a network admin could be expected to have the ability to configure firewall rules.
In order to determine if network traffic adheres to expected usage and complies with technical standards, an organization would use a device that provides which functionality?
A.
Stateful packet filtering
B.
Signature matching
C.
Protocol anomaly detection
D.
CRC checking
E.
Forward error correction
Protocol anomaly detection
In addition to standards compliance, Protocol Anomaly Detection determines whether data within the protocol adheres to expected usage. Even if a communication stream complies with a protocol standard, the way in which the protocol is being used may be inconsistent with what is expected. Perimeter devices that perform protocol anomaly detection contain in-depth knowledge of protocol standards and expected usage and are able to detect traffic that does not comply with those guidelines.
Who is ultimately responsible for approving methods and controls that will reduce any potential risk to an organization?
A.
Senior Management
B.
Data Owner
C.
Data Custodian
D.
Security Auditor
Security Auditor
When running a Nmap UDP scan, what would the following output indicate?
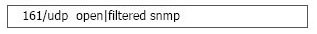
A.
The port may be open on the system or blocked by a firewall
B.
The router in front of the host accepted the request and sent a reply
C.
An ICMP unreachable message was received indicating an open port
D.
An ACK was received in response to the initial probe packet
The port may be open on the system or blocked by a firewall
When Nmap shows an “open filtered” response for the scan results, this indicates a couple of different reasons. The port could be open but a firewall could be blocking the use ACK flags; only TCP packets do.
Which statement below is the MOST accurate about insider threat controls?
A.
Classification of information assets helps identify data to protect.
B.
Security awareness programs have a minimal impact on reducing the insider threat.
C.
Both detective and preventative controls prevent insider attacks
D.
Rotation of duties makes an insider threat more likely
E.
Separation of duties encourages one employee to control a great deal of information
Classification of information assets helps identify data to protect.
A company needs to classify its information as a key step in valuing it and knowing where to focus its protection.
Rotation of duties and separation of duties are both key elements in reducing the scope of information access and the ability to conceal malicious behavior.
Separation of duties helps minimize “empire building” within a company, keeping one individual from controlling a great deal of information, reducing the insider threat.
Security awareness programs can help other employees notice the signs of an insider attack and thus reduce the insider threat. Detection is a reactive method and only occurs after an attack occurs. Only preventative methods can stop or limit an attack.
A company wants to allow only company-issued devices to attach to the wired and wireless networks. Additionally, devices that are not up-to-date with OS patches need to be isolated from the rest of the network until they are updated. Which technology standards or protocols would meet these requirements?
A.
802.1x and Network Access Control
B.
Kerberos and Network Access Control
C.
LDAP and Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA)
D.
802.11i and Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA)
802.1x and Network Access Control
Which Unix administration tool is designed to monitor configuration changes to Cisco, Extreme and Foundry infrastructure devices?
A.
SNMP
B.
Netflow
C.
RANCID
D.
RMON
RANCID
Which of the following applies to newer versions of IOS that decrease their attack surface?
A.
Telnet cannot be enabled or used
B.
The Cisco Discovery Protocol has been removed
C.
More services are disabled by default
D.
Two-factor authentication is default required
More services are disabled by default
Recent versions of IOS have less services enabled by default, older versions vary but generally have more services (even those not needed) enabled by default; this increases the attack surface on the device.
Which of the following would be used in order to restrict software form performing unauthorized operations, such as invalid access to memory or invalid calls to system access?
A.
Perimeter Control
B.
User Control
C.
Application Control
D.
Protocol Control
E.
Network Control
Application Control
| Page 2 out of 9 Pages |
| Previous |