Topic 1: Exam Pool A
“HTTP/1.1 204 content” is returned when cur –I –x delete command is issued. Which situation has occurred?
A.
The object could not be located at the URI path.
B.
The command succeeded in deleting the object
C.
The object was located at the URI, but it could not be deleted
D.
The URI was invalid
The command succeeded in deleting the object
Explanation: HTTP Status 204 (No Content) indicates that the server has successfully fulfilled the request and that there is no content to send in the response payload body.
Which encryption hashing algorithm does NTP use for authentication?
A.
SSL
B.
MD5
C.
AES128
D.
AES256
MD5
Explanation: An example of configuring NTP authentication is shown below: Router1(config)#ntp authentication-key 2 md5 itexamanswersRouter1(config)#ntp authenticateRouter1(config)#ntp trusted-key 2
A customer requests a network design that supports these requirements:

Which protocol does the design include?
A.
HSRP version 2
B.
VRRP version 2
C.
GLBP
D.
VRRP version 3
VRRP version 3
Under which network conditions is an outbound QoS policy that is applied on a router WAN interface most beneficial?
A.
under interface saturation condition
B.
under network convergence condition
C.
under all network condition
D.
under traffic classification and marking conditions
under interface saturation condition
A customer has recently implemented a new wireless infrastructure using WLC-5520 at a site directly next to a large commercial airport. Users report that they intermittently lose WIFI connectivity, and troubleshooting reveals it is due to frequent channel changes. Which two actions fix this issue? (Choose two)
A.
Remove UNII-2 and Extended UNII-2 channels from the 5 Ghz channel list
B.
Restore the DCA default settings because this automatically avoids channel interference.
C.
Configure channels on the UNIk2 and the Extended UNII-2 sub-bands of the 5 Ghz band only
D.
Enable DFS channels because they are immune to radar interference
E.
Disable DFS channels to prevent interference with Doppler radar
Remove UNII-2 and Extended UNII-2 channels from the 5 Ghz channel list
Disable DFS channels to prevent interference with Doppler radar
What is the output of this code?

A.
username Cisco
B.
get_credentials
C.
username
D.
CISCO
CISCO

A.
Option A
B.
Option B
C.
Option C
D.
Option D
Option D
Refer to the exhibit.
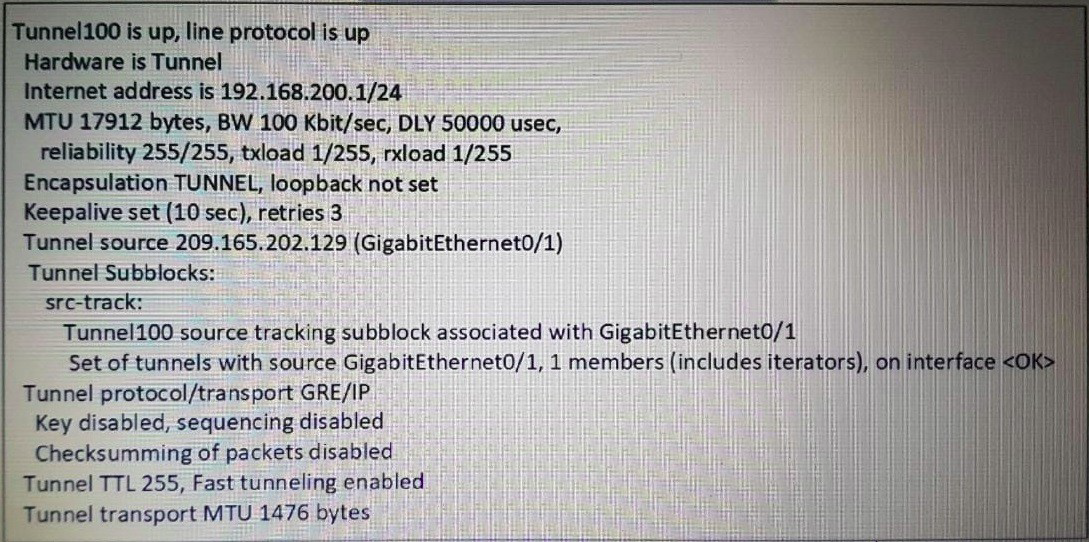
A network engineer configures a GRE tunnel and enters the show Interface tunnel command. What does the output confirm about the configuration?
A.
The keepalive value is modified from the default value.
B.
Interface tracking is configured.
C.
The tunnel mode is set to the default
D.
The physical interface MTU is 1476 bytes.
The tunnel mode is set to the default
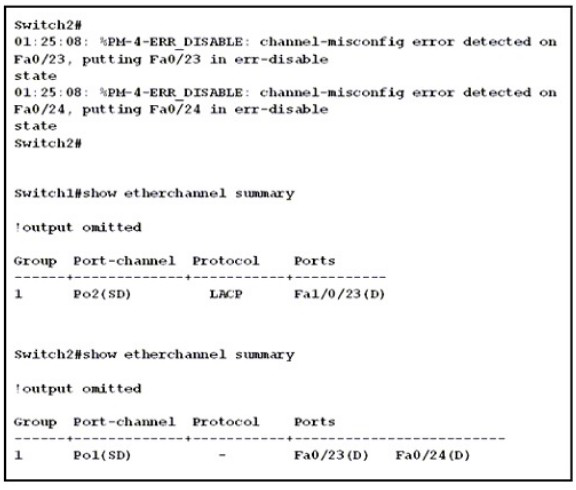
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is configuring an EtherChannel between Switch1 and Switch2 and notices the console message on switch2. Based on the output, which action resolves this issue?
A.
Configure less member ports on Switch2.
B.
Configure the same port channel interface number on both switches
C.
Configure the same EtherChannel protocol on both switches
D.
Configure more member ports on Switch1.
Configure the same EtherChannel protocol on both switches
Explanation: In this case, we are using your EtherChannel without a negotiation protocol on Switch2. As a result, if the opposite switch is not also configured for EtherChannel operation on the respective ports, there is a danger of a switching loop. The EtherChannel Misconfiguration Guard tries to prevent that loop from occuring by disabling all the ports bundled in the EtherChannel.
Which TCP setting is tuned to minimize the risk of fragmentation on a GRE/IP tunnel?
A.
MTU
B.
Window size
C.
MRU
D.
MSS
MSS
Explanation: The TCP Maximum Segment Size (TCP MSS) defines the maximum amount of data that a host is willing to accept in a single TCP/IP datagram. This TCP/IP datagram might be fragmented at the IP layer. The MSS value is sent as a TCP header option only in TCP SYN segments. Each side of a TCP connection reports its MSS value to the other side. Contrary to popular belief, the MSS value is not negotiated between hosts. The sending host is required to limit the size of data in a single TCP segment to a value less than or equal to the MSS reported by the receiving host.
TCP MSS takes care of fragmentation at the two endpoints of a TCP connection, but it does not handle the case where there is a smaller MTU link in the middle between these two endpoints. PMTUD was developed in order to avoid fragmentation in the path between the endpoints.
| Page 8 out of 84 Pages |
| Previous |