Topic 1: Exam Pool A
Which AP mode allows an engineer to scan configured channels for rogue access points?
A.
sniffer
B.
monitor
C.
bridge
D.
local
monitor
Refer to the exhibit.
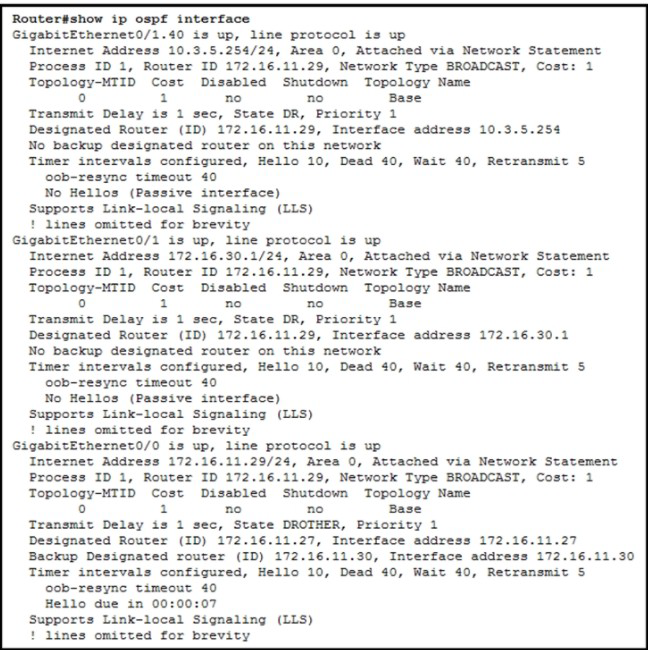
A network engineer configures OSPF and reviews the router configuration. Which interface or interface or interface are able to establish OSPF adjacency?
A.
GigabitEthemet0/1 and GigabitEthernet0/1.40
B.
only GigabitEthernet0/1
C.
only GigabttEthernet0/0
D.
Gigabit Ethernet0/0 and GigabitEthemet0/1
only GigabttEthernet0/0
Which method creates an EEM applet policy that is registered with EEM and runs on demand or manually?
A.
event manager applet ondemand
event register
action 1.0 syslog priority critical msg 'This is a message from ondemand'
B.
event manager applet ondemand
event manual
action 1.0 syslog priority critical msg 'This is a message from ondemand'
C.
event manager applet ondemand
event none
action 1.0 syslog priority critical msg 'This is a message from ondemand'
D.
event manager applet ondemand
action 1.0 syslog priority critical msg 'This is a message from ondemand'
event manager applet ondemand
event none
action 1.0 syslog priority critical msg 'This is a message from ondemand'
Explanation: An EEM policy is an entity that defines an event and the actions to be taken when that event occurs. There are two types of EEM policies: an applet or a script. An applet is a simple form of policy that is defined within the CLI configuration. answer 'event manager applet ondemand event register action 1.0 syslog priority critical msg ‘This is a message from ondemand’
<="" p="" style="box-sizing: border-box;">
There are two ways to manually run an EEM policy. EEM usually schedules and runs policies on the basis of an event specification that is contained within the policy itself. The event none command allows EEM to identify an EEM policy that can be manually triggered. To run the policy, use either the action policy command in applet configuration mode or the event manager run command in privileged EXEC mode.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/eem/configuration/xe-3s/eem-xe-3s-book/eem-policy-cli.html

Which command must be applied to R2 for an OSPF neighborship to form?
A.
network 20.1.1.2.0.0.0.0 area 0
B.
network 20.1.1.2 255.255.0.0. area 0
C.
network 20.1.1.2.0.0.255.255 area 0
D.
network 20.1.1.2 255.255.255 area 0
network 20.1.1.2.0.0.0.0 area 0
Explanation: The network 20.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 command on R2 did not cover the IP address of Fa1/1 interface of R2 so OSPF did not run on this interface. Therefore we have to use the command network 20.1.1.2 0.0.255.255 area 0 to turn on OSPF on this interface.
Note: The command network 20.1.1.2 0.0.255.255 area 0 can be used too so this answer is also correct but answer C is the best answer here. The network 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 area 0 command on R1 will run OSPF on all active
An engineer is troubleshooting the Ap join process using DNS. Which FQDN must be resolvable on the network for the access points to successfully register to the WLC?
A.
wlcbostname.domain.com
B.
Cisco-capwap-controller.domain.com
C.
ap-manager.domain.com
D.
primary-wlc.domain.com
Cisco-capwap-controller.domain.com
Explanation: DNS: If you have configured your DHCP server to provide both option 006 (DNS server address) and option 015 (domain name) information, the AP can obtain WLC addresses from the DNS server. The process works as follows:
1. The AP gets its IP address from DHCP with options 6 and 15 configured.
2. The AP can obtain the IP address of the DNS server from the DHCP option.
3. The AP uses this information to perform a hostname lookup using CISCO-CAPWAPCONTROLLER.<localdomain>, which resolves to available WLC management interface IP
addresses (IPv4 or IPv6, or both).
4. The AP can then perform a directed message to associate to responsive WLCs. To prevent all APs from joining a single controller based on a DNS name resolution, the domain name may vary; this is what is done to dispatch APs to different controllers across the enterprise network, based on different domain names that are configured in their respective DNS scopes.
Which three methods does Cisco DNA Centre use to discover devices? (Choose three)
A.
CDP
B.
SNMP
C.
LLDP
D.
ping
E.
NETCONF
F.
a specified range of IP addresses
CDP
LLDP
a specified range of IP addresses

Which two operations are valid for RESTCONF? (Choose two.)
A.
HEAD
B.
REMOVE
C.
PULL
D.
PATCH
E.
ADD
F.
PUSH
HEAD
PATCH
Explanation: RESTCONF operations include OPTIONS, HEAD, GET, POST, PATCH, DELETE.
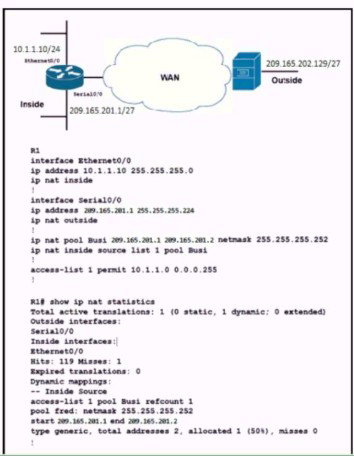
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer configures NAT on R1 and enters the show command to verity the configuration What does the output confirm?
A.
The first pocket triggered NAT to add on entry to NAT table
B.
R1 is configured with NAT overload parameters
C.
A Telnet from 160.1.1 1 to 10.1.1.10 has been initiated
D.
R1 to configured with PAT overload parameters
The first pocket triggered NAT to add on entry to NAT table
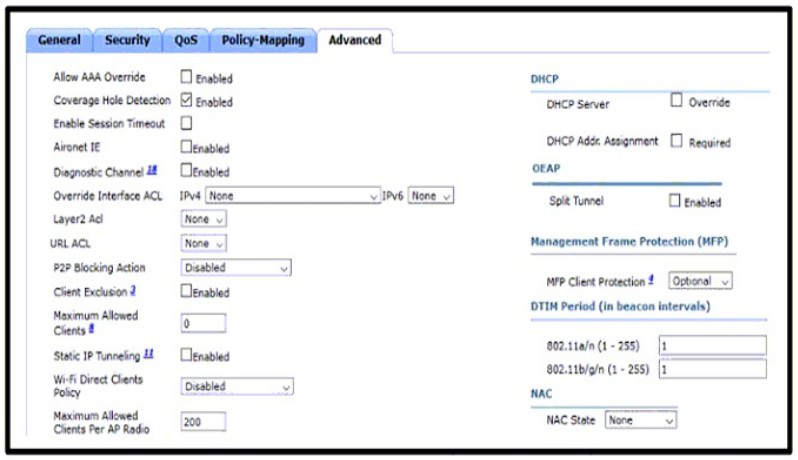
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is investigating why guest users are able to access other guest user devices when the users are connected to the customer guest WLAN. What action resolves this issue?
A.
implement MFP client protection
B.
implement split tunneling
C.
implement P2P blocking
D.
implement Wi-Fi direct policy
implement P2P blocking
Explanation: This control determines whether the Wireless LAN Controller is configured to prevent clients connected to the same Wireless Local Area Controller from communicating with each other.
Wireless Client Isolation prevents wireless clients from communicating with each other over the RF. Packets that arrive on the wireless interface are forwarded only out the wired interface of an Access Point. One wireless client could potentially compromise another client sharing the same wireless network.
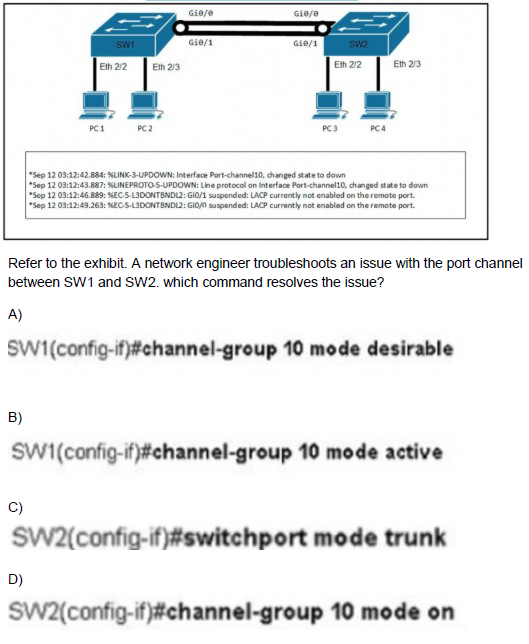
A.
Option A
B.
Option B
C.
Option C
D.
Option D
Option B
| Page 4 out of 84 Pages |
| Previous |