Refer to the exhibit.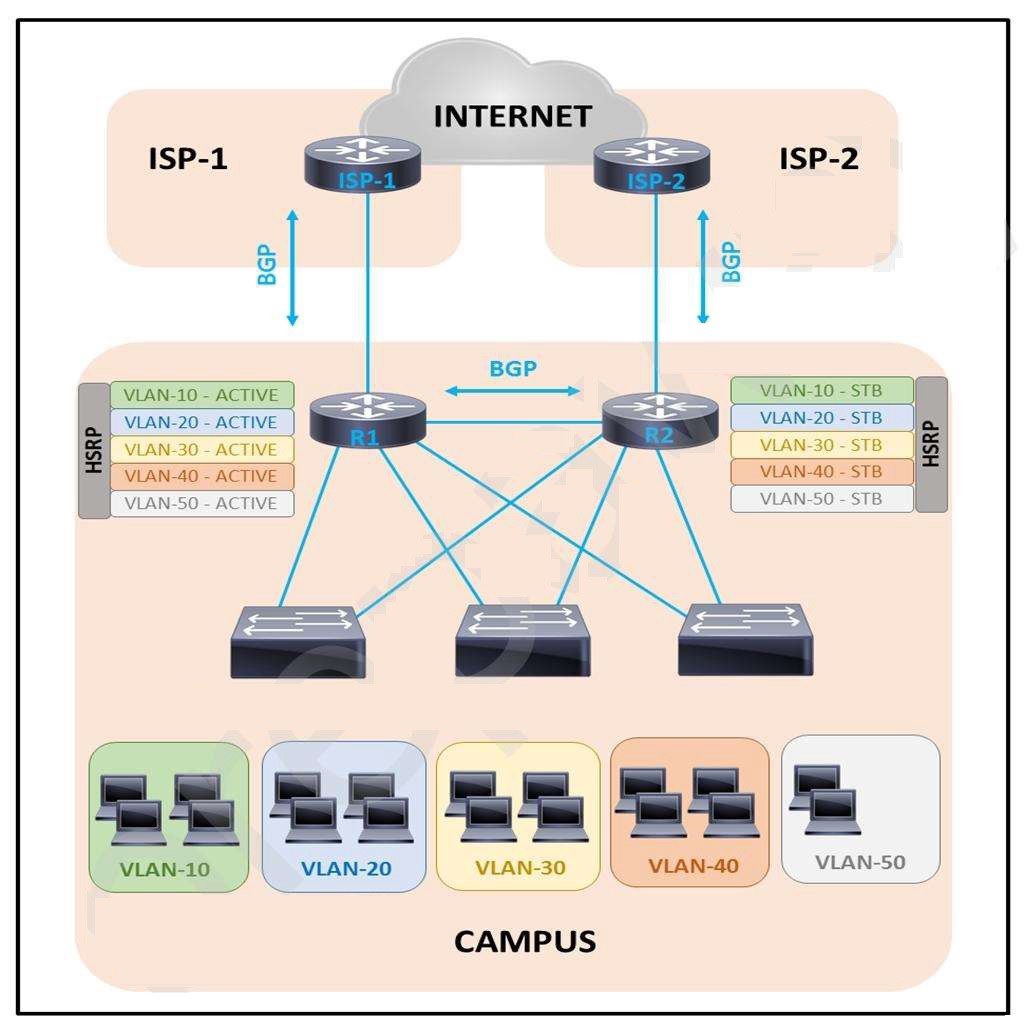
A customer is running HSRP on the core routers. Over time the company has grown and
requires more
network capacity. In the current environment, some of the downstream interfaces are
almost fully utilized, but
others are not. Which solution improves the situation?
A.
Make router R2 active for half of the VLANs.
B.
Add more interfaces to R1 and R2.
C.
Configure port channel toward downstream switches.
D.
Enable RSTP on the downstream switches.
Make router R2 active for half of the VLANs.
Which nonproprietary mechanism can be used to automate rendezvous point distribution in
a large PIM domain?
A.
Embedded RP
B.
BSR
C.
Auto-RP
D.
Static RP
BSR
Refer to the exhibit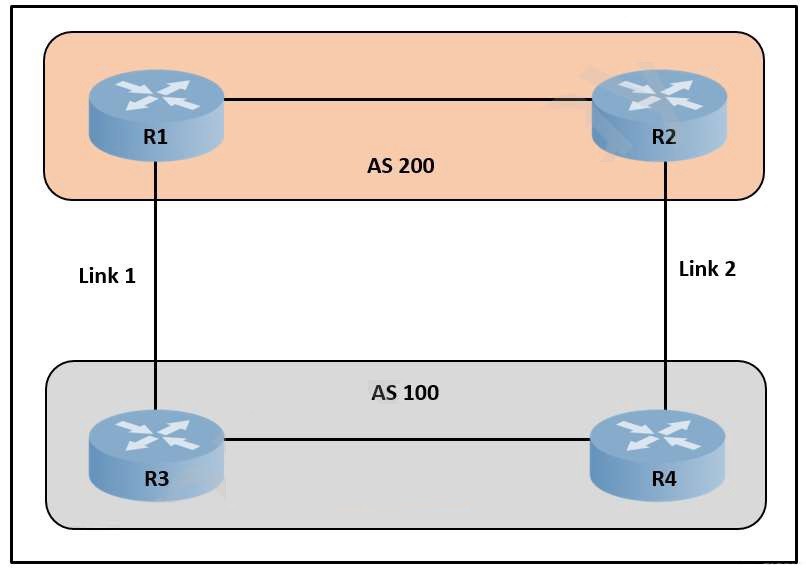
C9ACDC725EA850EC2476EE1E
A network engineer is designing a network for AS100. The design should ensure that all traffic enters AS100 via link 1 unless there is a network failure. In the event of a failure, link 2 should function as the path for incoming traffic. Which solution should the design include?
A.
Modify the next-hop attribute on R3.
B.
Use AS-Path prepending on R3.
C.
Modify the next-hop attribute on R4.
D.
Use AS-Path prepending on R4
Use AS-Path prepending on R4
An infrastructure team is concerned about the shared memory utilization of a device, and
for this reason, they need to monitor the device state. Which solution limits impact on the
device and provides the required data?
A.
IPFIX
B.
static telemetry
C.
on-change subscription
D.
periodic subscription
on-change subscription
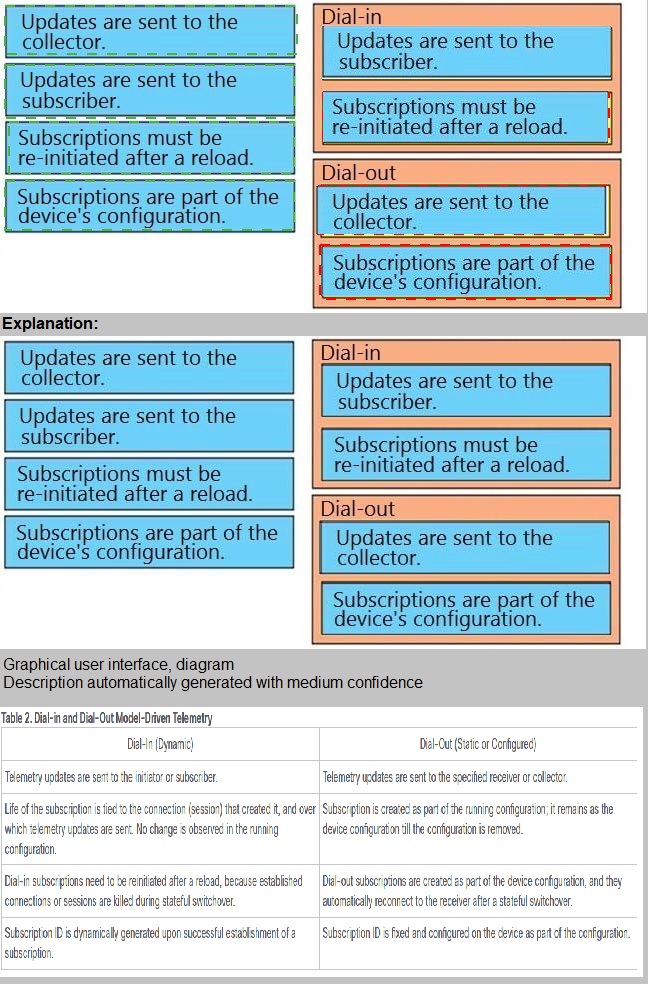
Explanation: There are two types of subscriptions: periodic and on-change. With periodic
subscription, data is streamed out to the destination at the configured interval. It
continuously sends data for the lifetime of that subscription. With on-change, data is
published only when a change in the data occurs such as when an interface or OSPF
neighbor goes down. https://developer.cisco.com/docs/ios-xe/#!streaming-telemetry-quickstart-
guide/streaming-telemetry
An engineer is creating a design to enable IPv6 to run on an existing IPv4 IS-IS network.
The IPv4 and IPv6 topologies will match exactly, and the engineer plans to use the same
router levels for each protocol per interface. Which IS-IS design is required?
A.
single topology without enabling transition feature
B.
single topology with transition feature enabled
C.
multi topology with transition feature enabled
D.
multi topology without enabling transition feature
multi topology with transition feature enabled
Explanation: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/iosxml/
ios/iproute_isis/configuration/15-mt/irs-15-mt-book/ip6-route-multi-isis.html
An engineer is designing an enterprise campus network. The LAN infrastructure consists of
switches from multiple vendors, and Spanning Tree must be used as a Layer 2 loop
prevention mechanism. All configured
VLANs must be grouped in two SIP instances. Which standards-based Spanning Tree
technology supports this design solution?
A.
MSTP
B.
RSTP
C.
Rapid PVST
D.
STP
MSTP
An ISP provides Layer 3 VPN service over MPLS to a customer with four branches and
multiple CE routers at
each branch. To exchange the routes that are learned from the CE routers, which BGP
address family should
the ISP activate among the PE routers?
A.
address-family multicast
B.
L2VPN EVPN
C.
VPNv4 unicast
D.
IPv4 unicast
VPNv4 unicast
Drag and drop the model driven telemetry characteristics from the left onto the mode they belong to on the right.
A network engineer must segregate three interconnected campus networks using IS-IS
routing. A two-layer hierarchy must be used to support large routing domains and to avoid
more specific routes from each campus network being advertised to other campus network
routers automatically. Which two actions does the engineer take to accomplish this
segregation? (Choose two.)
A.
Designate two IS-IS routers as BDR routers at the edge of each campus, and configure
one BDR for all Level 1 routers and one BDR for all Level 2 routers.
B.
Designate two IS-IS routers from each campus to act as Level 1/Level 2 backbone
routers at the edge of each campus network.
C.
Assign the same IS-IS NET value for each campus, and configure internal campus
routers with Level 1/ Level 2 routing.
D.
Utilize different MTU values for each campus network segment. Level 2 backbone
routers must utilize a larger MTU size of 9216.
E.
Assign a unique IS-IS NET value for each campus, and configure internal campus
Designate two IS-IS routers from each campus to act as Level 1/Level 2 backbone
routers at the edge of each campus network.
Assign a unique IS-IS NET value for each campus, and configure internal campus
When a first hop redundancy solution is designed, which protocol ensures that load balancing occurs over multiple routers using a single virtual IP address and multiple virtual MAC addresses?
A.
GLBP
B.
IRDP
C.
VRRP
D.
HSRP
GLBP
| Page 4 out of 21 Pages |
| Previous |