Drag and drop the characteristics from the left onto the Yang model they describe on the right. Select and Place: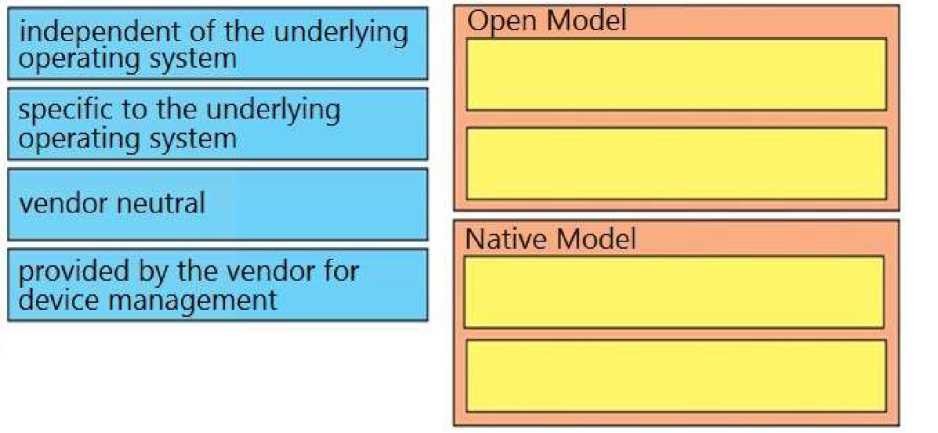
Refer to the exhibit.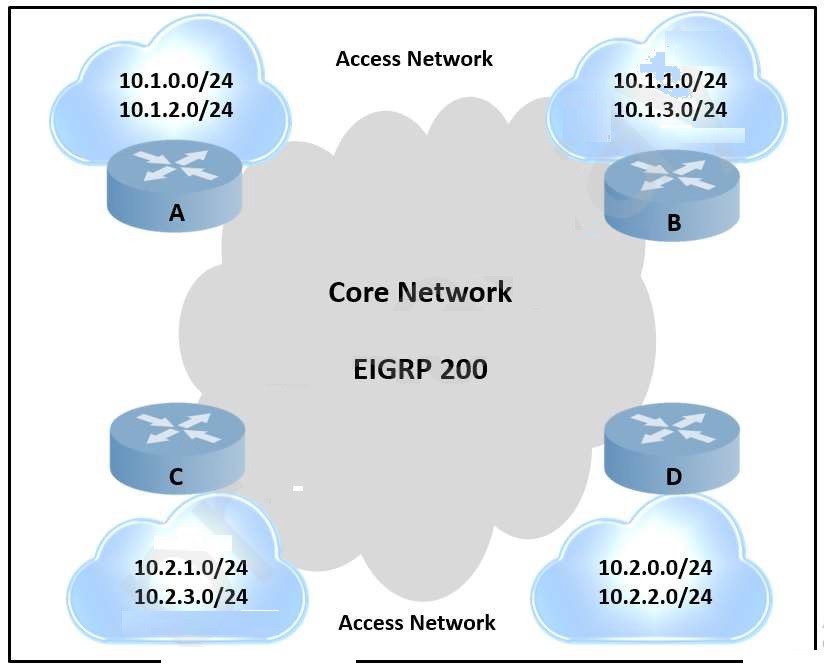
An engineer is designing a routing solution for a customer. The design must ensure that a
failure of network
10.1.0.0/24, 10.1.2.0/24, 10.2.1.0/24, or 10.2.3.0/24 does not impact the core. It also
requires fast convergence
time during any link failover in the core or access networks. Which solution must the
engineer select?
A.
Add aggregation layer between core and access networks.
B.
Enable graceful restart on routers A and C.
C.
Enable FRR for the connected networks of routers A and C.
D.
Enable summarization on routers A and C.
Enable FRR for the connected networks of routers A and C.
Which OSPF area blocks LSA Type 3, 4 and 5, but allows a default summary route?
A.
normal
B.
stub
C.
NSSA
D.
totally stubby
totally stubby
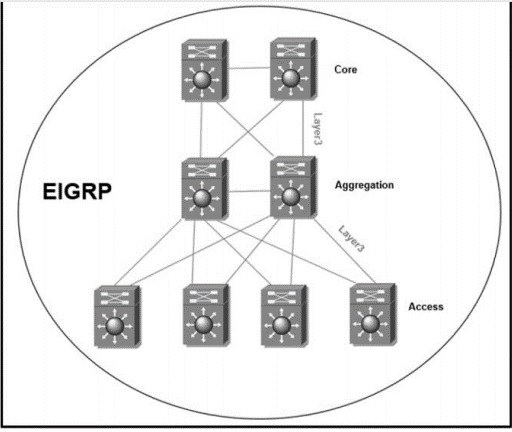
Refer to the exhibit. The full EIGRP routing table is advertised throughout the network.
Currently, users experience data loss when any one link in the network fails. An architect
optimizes the network to reduce the impact when a link fails. Which solution should the
architect include in the design?
A.
Run BFD on the inter links between EIGRP neighbors.
B.
Summarize the access layer networks from each access layer switch toward the aggregation layer.
C.
Reduce the default EIGRP hello interval and hold time.
D.
Summarize the access layer networks from the aggregation layer toward the core layer.
Run BFD on the inter links between EIGRP neighbors.
An engineer is working for a large cable TV provider that requires multiple sources
streaming video on different channels using multicast with no rendezvous point. Which multicast protocol meets these requirements?
A.
PIM-SM
B.
PIM-SSM
C.
any-source multicast
D.
BIDIR-PIM
PIM-SSM
Explanation: PIM-SSM is suitable for when well-known sources exist within the local PIM
domain and for broadcast applications. Also, PIM-SSM eliminates the RPs and shared
trees
Which two techniques improve the application experience in a Cisco SD-WAN design? (Choose two.)
A.
utilizing forward error correction
B.
implementing a stateful application firewall
C.
implementing AMP
D.
utilizing quality of service
E.
implementing Cisco Umbrella
utilizing forward error correction
utilizing quality of service
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en/us/solutions/collateral/enterprise-networks/sdwan/
nb-06-cisco-sd-wan-ebook-cte-en.pdf slide 33
The customer solution requires QoS to support streaming multimedia over a WAN. An architect chooses to use Per-Hop Behavior. Which solution should the engineer use to of mark traffic traveling between branch sites?
A.
LLQ with DSCP EF
B.
CBWFQ with DSCP AF3
C.
CBWFQ with DSCP AF2
D.
LLQ with DSCP AF4
LLQ with DSCP EF
What is the purpose of a control plane node in a Cisco SD-Access network fabric?
A.
to maintain the endpoint database and mapping between endpoints and edge nodes
B.
to detect endpoints in the fabric and inform the host tracking database of EID-to-fabricedge node bindings
C.
to identify and authenticate endpoints within the network fabric
D.
to act as the network gateway between the network fabric and outside networks
to detect endpoints in the fabric and inform the host tracking database of EID-to-fabricedge node bindings
Explanation: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/CVD/Campus/cisco-sdadesign-
guide.html
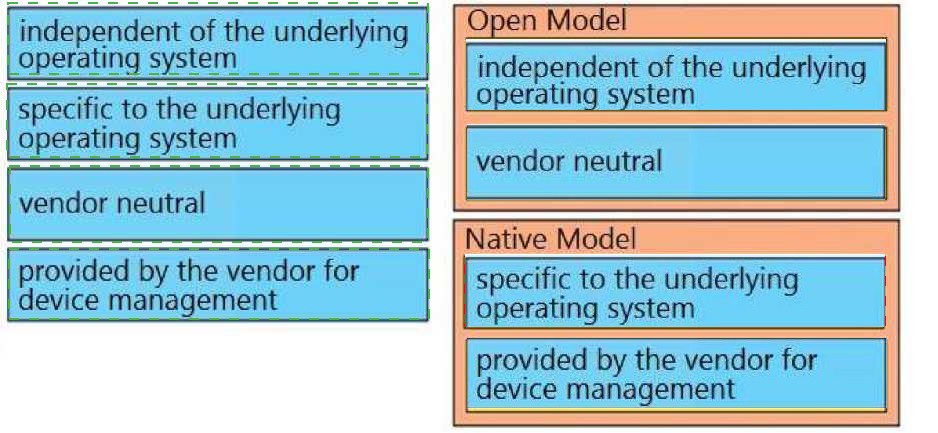
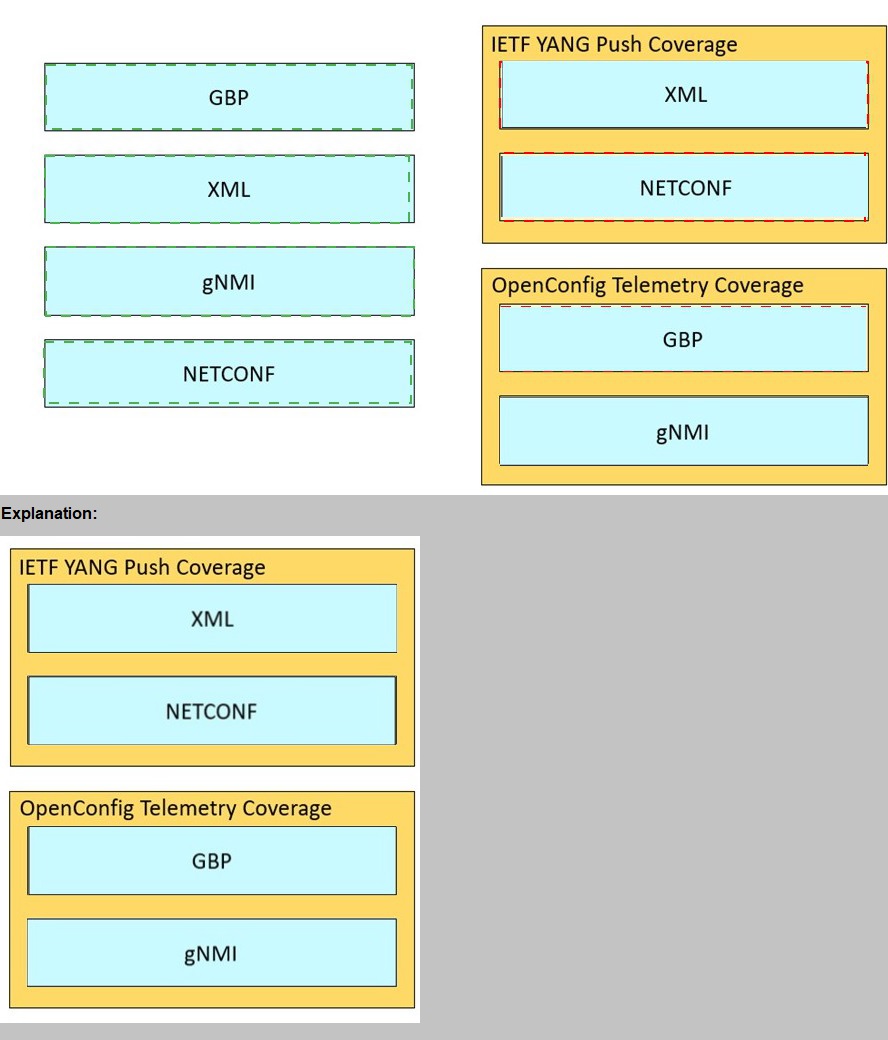
Drag and drop the elements from the left onto the YANG models where they and used on the right.
Which two statements describe source trees in a multicast environment? (Choose two.)
A.
Source trees guarantee the minimum amount of network latency for forwarding
multicast traffic
B.
Source trees create an optimal path between the source and the receivers
C.
Source trees use a single common root placed at some chosen point in the
network
D.
Source trees can introduce latency in packet delivery
Source trees guarantee the minimum amount of network latency for forwarding
multicast traffic
Source trees create an optimal path between the source and the receivers