Topic 1, Exam Pool A
Which two statements about VRF-Lite configurations are true? (Choose two.)
A.
They support the exchange of MPLS labels
B.
Different customers can have overlapping IP addresses on different VPNs
C.
They support a maximum of 512.000 routes
D.
Each customer has its own dedicated TCAM resources
E.
Each customer has its own private routing table
F.
They support IS-IS
Different customers can have overlapping IP addresses on different VPNs
Each customer has its own private routing table
A network engineer is investigating a flapping (up/down) interface issue on a core switch that is synchronized to an NTP server. Log output currently does not show the time of the flap. Which command allows the logging on the switch to show the time of the flap according to the clock on the device?
A.
service timestamps log uptime
B.
clock summer-time mst recurring 2 Sunday mar 2:00 1 Sunday nov 2:00
C.
service timestamps log datetime localtime show-timezone
D.
clock calendar-valid
service timestamps log datetime localtime show-timezone
During the maintenance window an administrator accidentally deleted the Telnet-related configuration that permits a Telnet connection from the inside network (Eth0/0) to the outside of the networking between Friday – Sunday night hours only. Which configuration resolves the issue?

A.
Option A
B.
Option B
C.
Option C
D.
Option D
Option C
Refer to the exhibit.
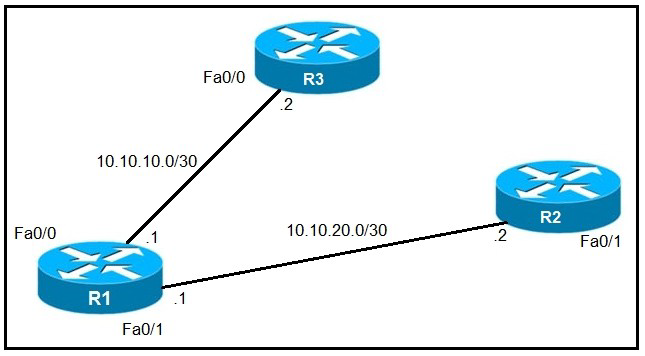
An IP SLA was configured on router R1 that allows the default route to be modified in the event that Fa0/0 loses reachability with the router R3 Fa0/0 interface. The route has changed to flow through router R2. Which debug command is used to troubleshoot this issue?
A.
debug ip flow
B.
debug ip sla error
C.
debug ip routing
D.
debug ip packet
debug ip routing
Explanation:
debug ip routing This command enables debugging messages related to the routing table.
Refer to the exhibit.

An administrator noticed that after a change was made on R1, the timestamps on the system logs did not match the clock. What is the reason for this error?
A.
An authentication error with the NTP server results in an incorrect timestamp.
B.
The keyword localtime is not defined on the timestamp service command.
C.
The NTP server is in a different time zone.
D.
The system clock is set incorrectly to summer-time hours.
The keyword localtime is not defined on the timestamp service command.
Which protocol is used to determine the NBMA address on the other end of a tunnel when mGRE is used?
A.
NHRP
B.
IPsec
C.
MP-BGP
D.
OSPF
NHRP
Which protocol does MPLS use to support traffic engineering?
A.
Tag Distribution Protocol (TDP)
B.
Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
C.
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
D.
Label Distribution Protocol (LDP)
Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
Refer to the exhibit.
An engineer is trying to generate a summary route in OSPF for network 10.0.0.0/8, but the summary route does not show up in the routing table. Why is the summary route missing?
A.
The summary-address command is used only for summarizing prefixes between areas.
B.
The summary route is visible only in the OSPF database, not in the routing table.
C.
There is no route for a subnet inside 10.0.0.0/8, so the summary route is not generated
D.
The summary route is not visible on this router, but it is visible on other OSPF routers in the same area.
There is no route for a subnet inside 10.0.0.0/8, so the summary route is not generated
Explanation:
The summary-address is only used to create aggregate addresses for OSPF at an autonomous system boundary. It means this command should only be used on the ASBR when you are trying to summarize externally redistributed routes from another protocol domain or you have a NSSA area. But a requirement to create a summarized route is:
The ASBR compares the summary route’s range of addresses with all routes redistributed into OSPF on that ASBR to find any subordinate subnets (subnets that sit inside the summary route range). If at least one subordinate subnet exists, the ASBR advertises the summary route.
Which configuration enabled the VRF that is labeled “Inet” on FastEthernet0/0?
A.
R1(config)# ip vrf Inet
R1(config-vrf)#interface FastEthernet0/0
R1(config-if)#ip vrf forwarding Inet
B.
R1(config)#router ospf 1 vrf Inet
R1(config-router)#ip vrf forwarding FastEthernet0/0
C.
R1(config)#ip vrf Inet FastEthernet0/0
D.
R1(config)# ip vrf Inet
R1(config-vrf)#ip vrf FastEthernet0/0
R1(config)# ip vrf Inet
R1(config-vrf)#interface FastEthernet0/0
R1(config-if)#ip vrf forwarding Inet
Users were moved from the local DHCP server to the remote corporate DHCP server. After the move, none of the users were able to use the network. Which two issues will prevent this setup from working properly? (Choose two)
A.
Auto-QoS is blocking DHCP traffic.
B.
The DHCP server IP address configuration is missing locally
C.
802.1X is blocking DHCP traffic
D.
The broadcast domain is too large for proper DHCP propagation
E.
The route to the new DHCP server is missing
The DHCP server IP address configuration is missing locally
The route to the new DHCP server is missing
| Page 1 out of 57 Pages |