Topic 1: Exam Pool A
desc about topic
In software-defined architecture, which place handles switching for traffic through a Cisco
router?
A.
Control
B.
Management
C.
Data
D.
application
Data
Explanation: Data plane—Handles all the data traffic. The basic functionality of a Cisco
NX-OS device is to forward packets from one interface to another. The packets that are not
meant for the switch itself are called the transit packets. These packets are handled by the
data plane
Which type of address is the public IP address of a NAT device?
A.
outside global
B.
outsdwde local
C.
inside global
D.
insride local
E.
outside public
F.
inside public
inside global
Explanation: NAT use four types of addresses:* Inside local address – The IP address
assigned to a host on the inside network. The address is usually not an IP address
assigned by the Internet Network Information Center (InterNIC) or service provider.This
address is likely to be an RFC 1918 private address.* Inside global address – A legitimate
IP address assigned by the InterNIC or service provider that represents one or more inside
local IP addresses to the outside world.* Outside local address – The IP address of an
outside host as it is known to the hosts on the inside network.* Outside global address –
The IP address assigned to a host on the outside network. The owner of the host assigns
this address.
Which CRUD operation corresponds to the HTTP GET method?
A.
read
B.
update
C.
create
D.
delete
read
Explanation: GET: This method retrieves the information identified by the request URI. In
the context of the RESTful web services, this method is used to retrieve resources. This is
the method used for read operations (the R in CRUD).
https://hub.packtpub.com/crud-operations-rest/
Which type of wireless encryption is used for WPA2 in preshared key mode?
A.
TKIP with RC4
B.
RC4
C.
AES-128
D.
AES-256
AES-256
Explanation:
We can see in this picture we have to type 64 hexadecimal characters (256 bit) for the
WPA2 passphrase so we can deduce the encryption is AES-256, not AES-128.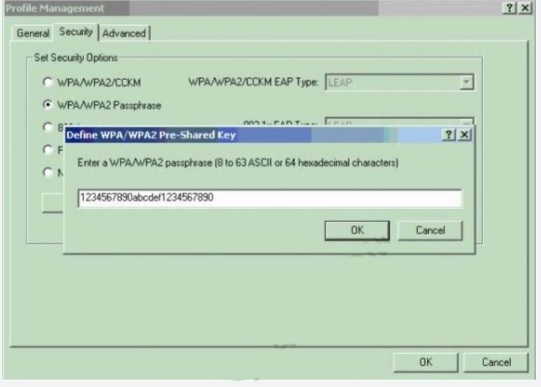
What is the difference regarding reliability and communication type between TCP and
UDP?
A.
TCP is reliable and is a connection-oriented protocol UDP is not reliable and is a connectionless protocol
B.
TCP is not reliable and is a connection-oriented protocol; UDP is reliable and is a connectionless protocol
C.
TCP is not reliable and is a connectionless protocol; UDP is reliable and is a connectionoriented
protocol
D.
TCP is reliable and is a connectionless protocol; UDP is not reliable and is a connectionoriented
protocol
TCP is reliable and is a connection-oriented protocol UDP is not reliable and is a connectionless protocol
A network administrator must enable DHCP services between two sites. What must be
configured for the router to pass DHCPDISCOVER messages on to the server?
A.
a DHCP Relay Agent
B.
DHCP Binding
C.
a DHCP Pool
D.
DHCP Snooping
a DHCP Relay Agent
Drag and drop the AAA functions from the left onto the correct AAA services on the right 
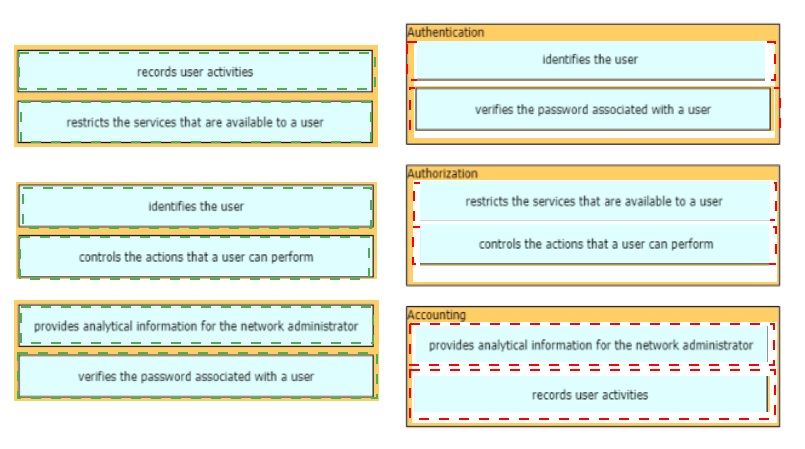
Which access layer threat-mitigation technique provides security based on identity?
A.
Dynamic ARP Inspection
B.
using a non-default native VLAN
C.
802.1x
D.
DHCP snooping
802.1x
Refer to the exhibit.
What is the result if Gig1/11 receives an STP BPDU?
A.
The port transitions to STP blocking
B.
The port transitions to the root port
C.
The port immediately transitions to STP forwarding.
D.
The port goes into error-disable state
The port goes into error-disable state
in Which way does a spine and-leaf architecture allow for scalability in a network when
additional access ports are required?
A.
A spine switch and a leaf switch can be added with redundant connections between them
B.
A spine switch can be added with at least 40 GB uplinks
C.
A leaf switch can be added with a single connection to a core spine switch.
D.
A leaf switch can be added with connections to every spine switch
A leaf switch can be added with connections to every spine switch
Explanation: Spine-leaf architecture is typically deployed as two layers: spines (such as
an aggregation layer), and leaves (such as an access layer). Spine-leaf topologies provide
high-bandwidth, low-latency, nonblocking server-to-server connectivity.
Leaf (aggregation) switches are what provide devices access to the fabric (the network of
spine and leaf switches) and are typically deployed at the top of the rack. Generally,
devices connect to the leaf switches.
Devices can include servers, Layer 4-7 services (firewalls and load balancers), and WAN
or Internet routers. Leaf switches do not connect to other leaf switches. In spine-and-leaf
architecture, every leaf should connect to every spine in a full mesh.
Spine (aggregation) switches are used to connect to all leaf switches and are typically
deployed at the end or middle of the row. Spine switches do not connect to other spine
switches.
| Page 8 out of 87 Pages |
| Previous |