Topic 2, Exam B
An engineer requires a scratch interface to actively attempt to establish a trunk link with a neighbor switch. What command must be configured?
A.
switchport mode trunk
B.
switchport mode dynamic desirable
C.
switchport mode dynamic auto
D.
switchport nonegotiate
switchport mode dynamic auto
Which action does the router take as rt forwards a packet through the network?
A.
The router replaces the source and desinaoon labels wth the sending router uterface
label as a source and the next hop router label as a desbnabon
B.
The router encapsulates the source and destination IP addresses with the sending
router P address as the source and the neighbor IP address as the destination
C.
The router replaces the original source and destination MAC addresses with the sending
router MAC address as the source and neighbor MAC address as the destination
D.
The router encapsulates the original packet and then includes a tag that identifies the
source router MAC address and transmit transparently to the destination
The router replaces the original source and destination MAC addresses with the sending
router MAC address as the source and neighbor MAC address as the destination
How do AAA operations compare regarding user identification, user services and access control?
A.
Authorization provides access control and authentication tracks user services
B.
Authentication identifies users and accounting tracks user services
C.
Accounting tracks user services, and authentication provides access control
D.
Authorization identifies users and authentication provides access control
Authentication identifies users and accounting tracks user services
What Is the path for traffic sent from one user workstation to another workstation on a separate switch In a Ihree-lter architecture model?
A.
access - core - distribution - access
B.
access - distribution - distribution - access
C.
access - core - access
D.
access -distribution - core - distribution - access
access -distribution - core - distribution - access
R1 has learned route 10.10.10.0/24 via numerous routing protocols. Which route is installed?
A.
route with the lowest cost
B.
route with the next hop that has the highest IP
C.
route with the shortest prefix length
D.
route with the lowest administrative distance
route with the lowest administrative distance
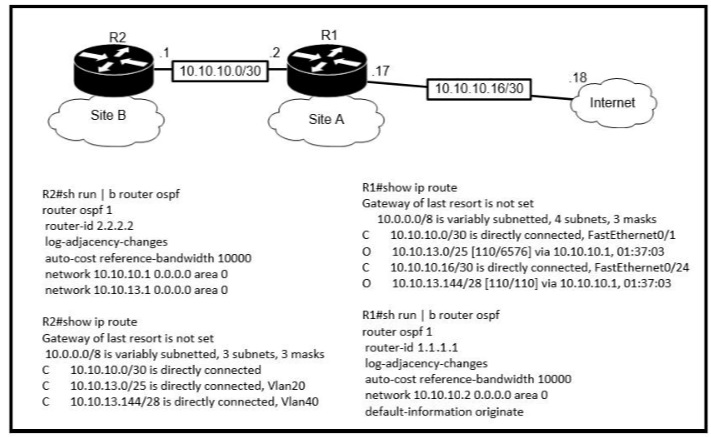
Refer to the exhibit.
If configuring a static default route on the router with the ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.13.0.1
120 command how does the router respond?
A.
It ignores the new static route until the existing OSPF default route is removed
B.
It immediately replaces the existing OSPF route in the routing table with the newly configured static route
C.
It starts load-balancing traffic between the two default routes
D.
It starts sending traffic without a specific matching entry in the routing table to
GigabitEthernetO/1
It ignores the new static route until the existing OSPF default route is removed
Explanation: Our new static default route has the Administrative Distance (AD) of 120,
which is bigger than the AD of OSPF External route (O*E2) so it will not be pushed into the
routing table until the current OSPF External route is removed.For your information, if you
don’t type the AD of 120 (using the command “ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.13.0.1”) then the
new static default route would replace the OSPF default route as the default AD of static
route is 1. You will see such line in the routing table:S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 10.13.0.1
What is the benefit of configuring PortFast on an interface?
A.
After the cable is connected, the interface uses the fastest speed setting available for
that cable type
B.
After the cable is connected, the interface is available faster to send and receive user data
C.
The frames entering the interface are marked with higher priority and then processed faster by a switch.
D.
Real-time voice and video frames entering the interface are processed faster
After the cable is connected, the interface is available faster to send and receive user data
How do traditional campus device management and Cisco DNA Center device
management differ in regards to deployment?
A.
Cisco DNA Center device management can deploy a network more quickly than
traditional campus device management
B.
Traditional campus device management allows a network to scale more quickly than
with Cisco DNA Center device management
C.
Cisco DNA Center device management can be implemented at a lower cost than most
traditional campus device management options
D.
Traditional campus device management schemes can typically deploy patches and
updates more quickly than Cisco DNA Center device management
Cisco DNA Center device management can deploy a network more quickly than
traditional campus device management
Drag and drop the descriptions from the left onto the configuration-management
technologies on the right.


Refer to the exhibit.
An engineer is bringing up a new circuit to the MPLS provider on the Gi0/1 interface of
Router1 The new circuit uses eBGP and teams the route to VLAN25 from the BGP path
What s the expected behavior for the traffic flow for route 10.10.13.0/25?
A.
Traffic to 10.10.13.0.25 is load balanced out of multiple interfaces
B.
Route 10.10.13.0/25 is updated in the routing table as being learned from interface
Gi0/1.
C.
Traffic to 10.10.13.0/25 is asymmeteical
D.
Route 10.10.13.0/25 learned via the GiO/0 interface remains in the routing table
Route 10.10.13.0/25 learned via the GiO/0 interface remains in the routing table
| Page 27 out of 87 Pages |
| Previous |