Topic 1: Exam Pool A
desc about topic
How do TCP and UDP differ in the way they guarantee packet delivery?
A.
TCP uses checksum, acknowledgement, and retransmissions, and UDP uses
checksums only.
B.
TCP uses two-dimensional parity checks, checksums, and cyclic redundancy checks
and UDP uses retransmissions only.
C.
TCP uses checksum, parity checks, and retransmissions, and UDP uses
acknowledgements only.
D.
TCP uses retransmissions, acknowledgement and parity checks and UDP uses cyclic
redundancy checks only.
TCP uses checksum, acknowledgement, and retransmissions, and UDP uses
checksums only.
what occurs to frames during the process of frame flooding?
A.
Frames are sent to every port on the switch in the same VLAN except from the
originating port
B.
Frames are sent to every port on the switch that has a matching entry in the MAC address table.
C.
Frames are sent to all ports, including those that are assigned to other VLANs.
D.
Frames are sent to every port on the switch in the same VLAN.
Frames are sent to every port on the switch in the same VLAN except from the
originating port
Drag and drop the 802.11 wireless standards from the left onto the matching statements on the right 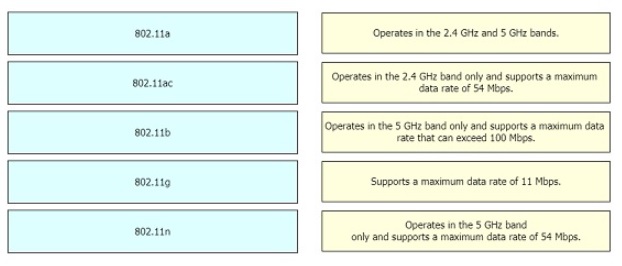
Which function is performed by the collapsed core layer in a two-tier architecture?
A.
enforcing routing policies
B.
marking interesting traffic for data polices
C.
attaching users to the edge of the network
D.
applying security policies
enforcing routing policies
Which type of attack can be mitigated by dynamic ARP inspection?
A.
worm
B.
malware
C.
DDoS
D.
man-in-the-middle
man-in-the-middle
How is the native VLAN secured in a network?
A.
separate from other VLANs within the administrative domain
B.
give it a value in the private VLAN range
C.
assign it as VLAN 1
D.
configure it as a different VLAN ID on each end of the link
separate from other VLANs within the administrative domain
Which network plane is centralized and manages routing decisions?
A.
policy plane
B.
management plane
C.
control plane
D.
data plane
control plane
Refer to the exhibit.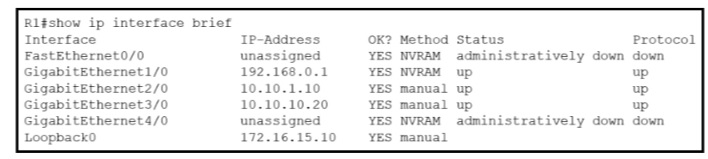
What does router R1 use as its OSPF router-ID?
A.
10.10.1.10
B.
10.10.10.20
C.
172.16.15.10
D.
192.168.0.1
172.16.15.10
Explanation: OSPF uses the following criteria to select the router ID:1. Manual
configuration of the router ID (via the “router-id x.x.x.x” command under OSPF router
configuration mode).2. Highest IP address on a loopback interface.3. Highest IP address
on a non-loopback and active (no shutdown) interface.
Refer to the exhibit.
Router R1 is running three different routing protocols. Which route characteristic is used by the router to forward the packet that it receives for destination IP 172.16.32.1?
A.
longest prefix
B.
metric
C.
cost
D.
administrative distance
longest prefix
Explanation:
https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/s/question/0D53i00000KszSlCAJ/administrative- distance-vs-longest-match-rule
What Is a syslog facility?
A.
Host that is configured for the system to send log messages
B.
password that authenticates a Network Management System to receive log messages
C.
group of log messages associated with the configured severity level
D.
set of values that represent the processes that can generate a log message
group of log messages associated with the configured severity level
Explanation: Cisco Community – Difference between logging level and logging facility
Post by ahmednaas
“The logging facility command basically tells the syslog server where to put the log
message. You configure the syslog server with something like:
local7.debug /var/adm/local7.log
Now, when you use the “logging facility local7” on your device, all messages with severity
“debug” or greater should be saved in /var/adm/local7.log.”
Example: on a switch, any process (CDP, SNMP, etc.) can generate a log message. On a
syslog server, the logging facility is the place where all received messages with the same
priority level are stored.
| Page 24 out of 87 Pages |
| Previous |