Topic 1: Exam Pool A
desc about topic
Which CRUD operation modifies an existing table or view?
A.
read
B.
create
C.
replace
D.
update
update
Router R1 must send all traffic without a matching routing-table entry to 192.168.1.1. Which configuration accomplishes this task?

A.
Option A
B.
Option B
C.
Option C
D.
Option D
Option C
What are two southbound APIs? (Choose two )
A.
OpenFlow
B.
NETCONF
C.
Thrift
D.
CORBA
E.
SC
OpenFlow
NETCONF
Explanation: OpenFlow is a well-known southbound API. OpenFlow defines the way the
SDN Controller should interact with the forwarding plane to make adjustments to the
network, so it can better adapt to changing business requirements.
The Network Configuration Protocol (NetConf) uses Extensible Markup Language (XML) to
install, manipulate and delete configuration to network devices.
Refer to the exhibit.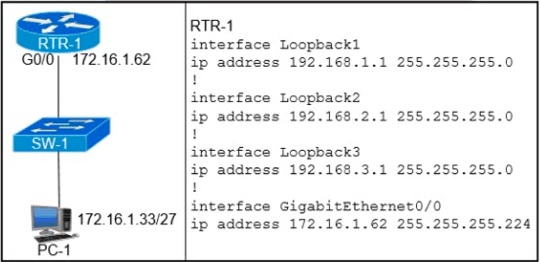
Which configuration on RTR-1 denies SSH access from PC-1 to any RTR-1 interface and
allows all other traffic?
A.
access-list 100 deny tcp host 172.16.1.33 any eq 22 access-list 100 permit ip any any
interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip access-group 100 in
B.
access-list 100 deny tcp host 172.16.1.33 any eq 22 access-list 100 permit ip any any
line vty 0 15 ip access-group 100 in
C.
access-list 100 deny tcp host 172.16.1.33 any eq 23 access-list 100 permit ip any any
interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip access-group 100 in
D.
access-list 100 deny tcp host 172.16.1.33 any eq 23 access-list 100 permit ip any any
line vty 0 15 ip access-group 100 in
access-list 100 deny tcp host 172.16.1.33 any eq 22 access-list 100 permit ip any any
line vty 0 15 ip access-group 100 in
Which network action occurs within the data plane?
A.
compare the destination IP address to the IP routing table.
B.
run routing protocols (OSPF, EIGRP, RIP, BGP)
C.
make a configuration change from an incoming NETCONF RPC
D.
reply to an incoming ICMP echo request
compare the destination IP address to the IP routing table.
Which IPv6 address block sends packets to a group address rather than a single address?
A.
2000::/3
B.
FC00::/7
C.
FE80::/10
D.
FF00::/8
FF00::/8
Explanation: FF00::/8 is used for IPv6 multicast and this is the IPv6 type of address the
question wants to ask.FE80::/10 range is used for link-local addresses. Link-local
addresses only used for communications within the local subnetwork (automatic address
configuration, neighbor discovery, router discovery, and by many routing protocols). It is
only valid on the current subnet.It is usually created dynamically using a link-local prefix of
FE80::/10 and a 64-bit interface identifier (based on 48-bit MAC address).
Which two actions are performed by the Weighted Random Early Detection mechanism?
(Choose two)
A.
It drops lower-priority packets before it drops higher-priority packets
B.
It can identify different flows with a high level of granularity
C.
It guarantees the delivery of high-priority packets
D.
It can mitigate congestion by preventing the queue from filling up
E.
it supports protocol discovery
It drops lower-priority packets before it drops higher-priority packets
It can mitigate congestion by preventing the queue from filling up
Explanation: Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) is just a congestion avoidance
mechanism. WRED drops packets selectively based on IP precedence. Edge routers
assign IP precedences to packets as they enter the network. When a packet arrives, the
following events occur:
1. The average queue size is calculated.2. If the average is less than the minimum queue
threshold, the arriving packet is queued.3. If the average is between the minimum queue
threshold for that type of traffic and the maximum threshold for the interface, the packet is
either dropped or queued, depending on the packet drop probability for that type of traffic.4.
If the average queue size is greater than the maximum threshold, the packet is dropped.
WRED reduces the chances of tail drop (when the queue is full, the packet is dropped) by
selectively dropping packets when the output interface begins to show signs of congestion
(thus it can mitigate congestion by preventing the queue from filling up). By dropping some
packets early rather than waiting until the queue is full, WRED avoids dropping large
numbers of packets at once and minimizes the chances of global synchronization. Thus,
WRED allows the transmission line to be usedfully at all times.
WRED generally drops packets selectively based on IP precedence. Packets with a higher
IP precedence are less likely to be dropped than packets with a lower precedence. Thus,
the higher the priority of a packet, the higher the probability that the packet will be delivered
Which attribute does a router use to select the best path when two or more different routes
to the same destination exist from two different routing protocols.
A.
dual algorithm
B.
metric
C.
administrative distance
D.
hop count
administrative distance
Explanation: Administrative distance is the feature used by routers to select the best path
when there are two or more different routes to the same destination from different routing
protocols. Administrative distance defines the reliability of a routing protocol.
What event has occurred if a router sends a notice level message to a syslog server?
A.
A TCP connection has been torn down
B.
An ICMP connection has been built
C.
An interface line has changed status
D.
A certificate has expired.
An interface line has changed status
Refer to the exhibit
What two conclusions should be made about this configuration? (Choose two )
A.
The designated port is FastEthernet 2/1
B.
This is a root bridge
C.
The spanning-tree mode is Rapid PVST+
D.
The spanning-tree mode is PVST+
E.
The root port is FastEthernet 2/1
The spanning-tree mode is Rapid PVST+
The root port is FastEthernet 2/1
| Page 2 out of 87 Pages |
| Previous |